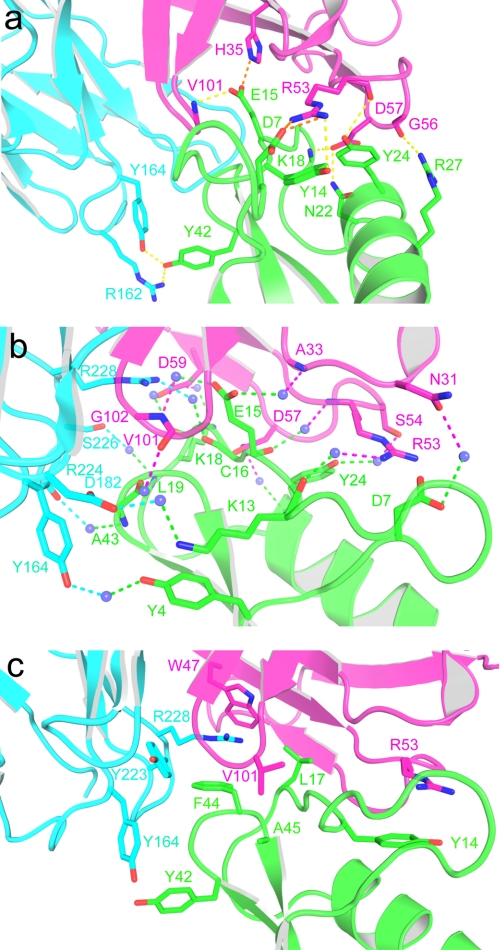
FIGURE 3.
The 9004G-Cn2 complex interface is mainly stabilized by charge-charge and hydrogen-bonding interactions involving five 9004G CDRs. a, view of the charge-charge and hydrogen-bonding interactions between residues of the interface of the 9004G-Cn2 complex. Toxin Cn2 is colored in green, and VH and VL domains of 9004G are colored in magenta and cyan, respectively. The yellow and orange dashes represent hydrogen and charge-charge interactions, respectively. b, water-mediated hydrogen bonds at the 9004G-Cn2 interface. There are 15 water molecules (blue spheres) that interact with the same number of residues at the 9004G-Cn2 interface. The magenta and cyan dashes represent hydrogen bonds between residues of the VH and VL domains, respectively. Residue Glu15 is attached to the binding site of 9004G trough three water-mediated hydrogen bonds between 3 residues of 9004G. The other water-mediated hydrogen bonds are distributed along the interface. c, hydrophobic, aromatic-aromatic (Y164L with Tyr42), and cation-π interactions (R53H with Tyr14 and R228L with Phe44) at the 9004G-Cn2 interface. Note that these interactions are less represented than polar interactions and are located in the periphery of the interface of the complex. Interactions at the interface of the 9004G-Cn2 complex include 6 hydrogen bonds, 4 charge-charge interactions, 15 water-mediated contacts, and 45 van der Waals contacts. Details of these interactions are shown in Table 2 and supplemental Tables S1 and S2.