FIGURE 3.
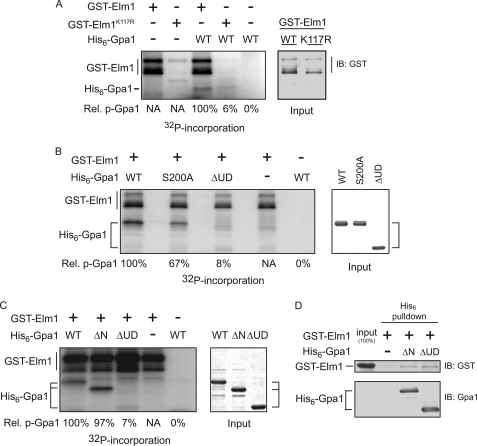
Elm1 is necessary and sufficient for Gpa1 phosphorylation. The association between Elm1 and Gpa1 as determined by copurification and by in vitro kinase assay. A, in vitro kinase assay with purified GST-Elm1 or catalytically inactive GST-Elm1K117R and purified recombinant Gpa1 in the presence of [γ32P]ATP (left panel) and GST-Elm1 input detected by immunoblot with anti-GST (right panel). B, in vitro kinase assay with GST-Elm1 and purified recombinant Gpa1 (WT), Gpa1S200A (S200A), or Gpa1Δ1-36,Δ129-236 (ΔUD) in the presence of [γ32P]ATP. Shown is the incorporation of radioactive phosphate (left panel) and Gpa1 input detected by Coomassie staining (right panel). C, in vitro kinase assay with GST-Elm1 and with purified recombinant His6-tagged Gpa1 (WT), Gpa1Δ1-36 (ΔN), or Gpa1Δ1-36, Δ129-236 (ΔUD) lacking the ubiquitinated subdomain. Shown is the incorporation of radioactive phosphate (left panel) and Gpa1 input detected by Coomassie gel staining (right panel). D, in vitro affinity purification using nickel affinity matrix and immunodetection of bound GST-Elm1 described in C. Relative 32P incorporation (Rel. p-Gpa1) is shown for Gpa1 and was calculated as follows: [32P signal/Coomassie signal]mutant/[32P signal/Coomassie signal]WT.