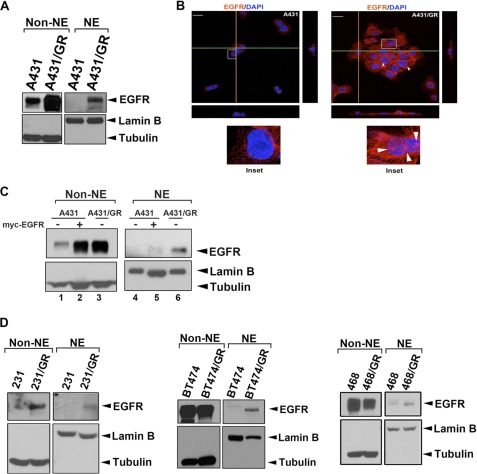
FIGURE 1.
Nuclear EGFR is involved in drug resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. A, A431 and A431/GR cells were subjected to cellular fractionation followed by WB analysis of cellular localization of EGFR. Levels of tubulin and lamin B were used as markers for cytosolic and nuclear fractions, respectively. B, immunofluorescence staining of EGFR (red) and DAPI (blue) was analyzed by confocal microscopy with z-stacks. Yellow and green lines represented corresponding points in the orthogonal planes, which confirmed distribution of the labels within the pictured cells after the summation of serial optical sections. The scale bar represents 10 μm. C, shown is EGFR overexpression in A431 cells followed by cellular fractionation. The cellular localization of EGFR was analyzed by WB. NE, nuclear extract. D, nuclear localization of EGFR in several gefitinib-resistant cell line pairs was analyzed as described in A.