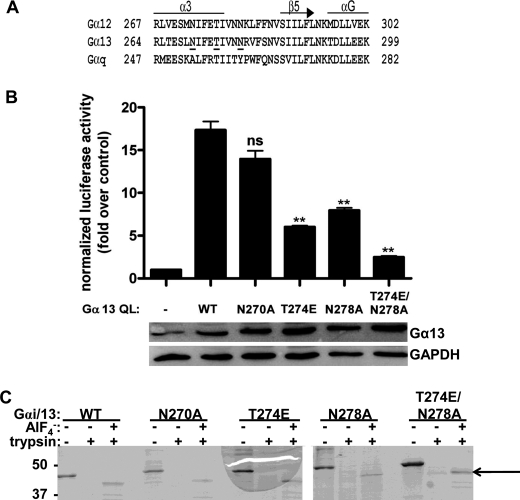
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of Gαi/13 mutants. A, a primary sequence alignment of murine Gα12, Gα13, and Gαq was generated using the program T-Coffee. Residues in Gα13 analyzed by site-directed mutagenesis in this study are underlined. Secondary structure was assigned based on the crystal structure of the Gα13/i1-p115 RH domain complex (Protein Data Bank entry 1SHZ) (17). B, the T274E and N278A mutations in Gα13 impair Rho activation in cells. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with empty vector or the indicated Gα13 QL construct. The luciferase activity of cell lysates was determined as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Total cell lysate was immunoblotted for either Gα13 or GAPDH. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of triplicate determinations from a single experiment, representative of three independent experiments with similar results. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's post-test. Statistically significant difference from Gα13 QL is shown as follows. ns, not significant; **, p < 0.01. C, Gαi/13 mutants can undergo activation-dependent conformational changes. Gαi/13 (wild type or mutant) was subjected to limited trypsin digestion in the presence or absence of AlF4−. After proteolysis, proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. The primary protected species is indicated with an arrow. The positions of molecular mass standards, in kDa, are shown on the left.