Figure 16.
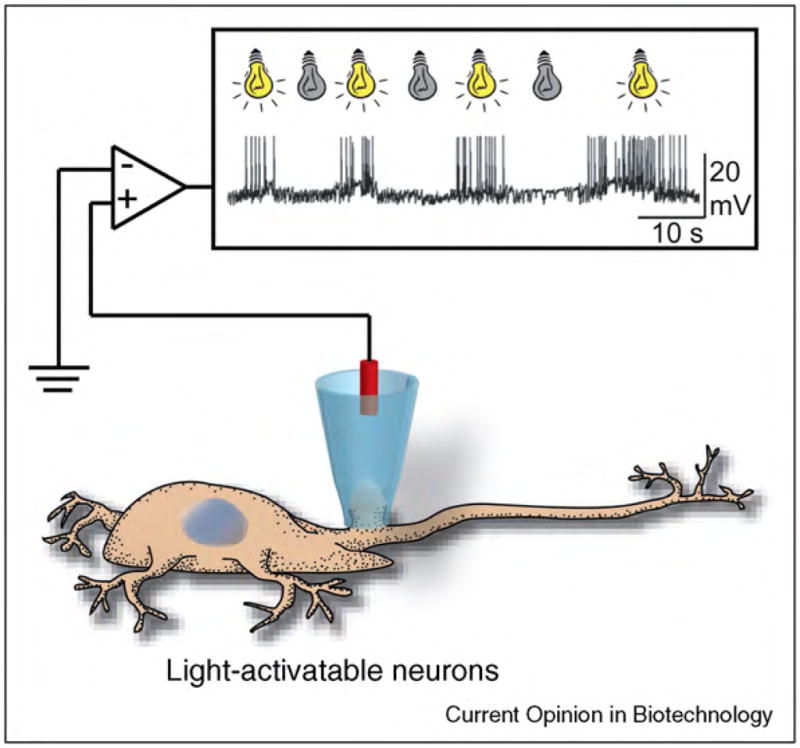
Cartoon illustrating the concept of remote control of neuronal firing by light. Expression of a light-activated ion channel (in this case, a modified potassium channel) in rat hippocampal neurons made these neurons sensitive to light as confirmed by current clamp recordings. Exposure to light with a wavelength of 500 nm resulted in spontaneous action potentials, while exposure to light with a wavelength of 380 nm silenced these action potentials. The inset shows a current versus time trace as adapted from reference [34••] with permission.
