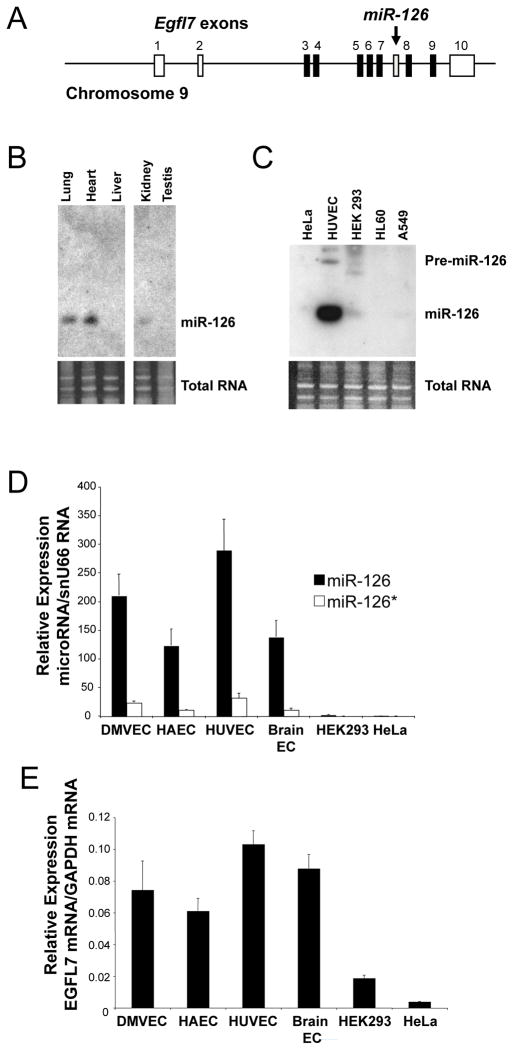
Figure 1.
Endothelial cells express miR-126 and its host gene Egfl7.
(A) Schematic of Egfl7/miR-126 locus. The host gene encoding EGFL7 also encodes the microRNA miR-126. Arrow points to intronic location of hsa-miR-126. White boxes: untranslated Egfl7 exons. Black boxes: translated Egfl7 exons. Gray box: miR-126 locus. (B) Tissue expression of miR-126 by Northern blotting. Total RNA was harvested from various mouse tissues and analyzed by Northern blotting for miR-126 RNA (top). Ethidium bromide staining of total RNA (below). (C) Cell expression of miR-126 by Northern blotting Total RNA was harvested from various cell types and analyzed by Northern blotting for miR-126 RNA (top). Ethidium bromide staining of total RNA (below). (D) Cell expression of miR-126 by Q-RT-PCR. Total RNA was harvested from various cell types and analyzed by quantitative-RT-PCR for miR-126 and miR-126* expressed relative to snu66 RNA (n = 2 ± S.D.). (E) Cell expression of EGFL7 mRNA by Q-RT-PCR. Total RNA was harvested from various cell types and analyzed by Q-RT-PCR for EGFL7 and GAPDH mRNA.