Table 4. Heritability estimates.
| Source | Description |
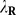
|
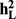
|
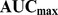
|
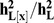
|
| NINDS | All PD | - | 0.229 (0.000–0.543) | 0.833 (0.500–0.935) | 0.077 (0.036- ) ) |
| 23andMe | All PD | - | 0.272 (0.229–0.315) | 0.857 (0.833–0.877) | 0.065 (0.056–0.077) |
| 23andMe | Early-onset PD (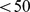 ) ) |
- | 0.306 (0.136–0.476) | 0.873 (0.766–0.933) | 0.057 (0.037–0.129) |
| 23andMe | Late-onset PD (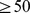 ) ) |
- | 0.285 (0.224–0.346) | 0.863 (0.830–0.890) | 0.062 (0.051–0.078) |
| [12] | Twin study; broad-definition PD | - | 0.30 (0.00–0.47) | 0.87 (0.50–0.93) | 0.059 (0.037- ) ) |
| [10] | Twin study; all PD | - | 0.274 (0.000–0.708) | 0.858 (0.000–0.976) | 0.064 (0.025- ) ) |
| [10] | Early-onset PD (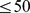 ) ) |
- |
 1.0 (0.33–1.00) 1.0 (0.33–1.00) |
0.996 (0.884–0.996) | 0.018 (0.018–0.053) |
| [10] | Late-onset PD (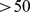 ) ) |
- | 0.068 (0.00–0.59) | 0.693 (0.000–0.958) | 0.258 (0.030- ) ) |
| [48] | Family study; all PD | - | 0.401 | 0.910 | 0.044 |
| [48] | Early-onset PD (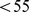 ) ) |
- | 0.169 | 0.793 | 0.104 |
| [48] | Late-onset PD (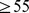 ) ) |
- | 0.453 | 0.926 | 0.039 |
| [73] | Family study; all PD | - | 0.60 (0.40–0.80) | 0.96 (0.91–0.99) | 0.029 (0.022–0.044) |
| [14] | Offsprings; all PD | 3.0 | 0.35 | 0.89 | 0.050 |
| [14] | Late-onset PD (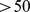 ) ) |
3.2 | 0.38 | 0.90 | 0.046 |
| [74] | Parents and siblings; all PD | 3.92 | 0.456 | 0.927 | 0.038 |
| [74] | Early-onset PD (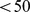 ) ) |
7.76 | 0.747 | 0.980 | 0.024 |
| [74] | Late-onset PD (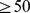 ) ) |
2.95 | 0.348 | 0.891 | 0.050 |
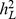 denotes the heritability of liability for PD, with a 95% CI provided where available. In the case of [10], confidence intervals were estimated via a bootstrap procedure based on numbers provided in the original paper. For studies that did not provide direct estimates of heritability, the relative recurrence risk ratio
denotes the heritability of liability for PD, with a 95% CI provided where available. In the case of [10], confidence intervals were estimated via a bootstrap procedure based on numbers provided in the original paper. For studies that did not provide direct estimates of heritability, the relative recurrence risk ratio 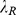 was used to estimate
was used to estimate 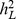 under the assumption of no shared environmental covariance (see Materials and Methods).
under the assumption of no shared environmental covariance (see Materials and Methods). 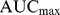 denotes the maximum theoretical AUC corresponding to the given heritability of liability, assuming a disease prevalence of 0.01.
denotes the maximum theoretical AUC corresponding to the given heritability of liability, assuming a disease prevalence of 0.01. 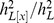 denotes the proportion of additive genetic variance explained by a genetic profile that achieves an AUC of 0.6 (see Materials and Methods).
denotes the proportion of additive genetic variance explained by a genetic profile that achieves an AUC of 0.6 (see Materials and Methods).
