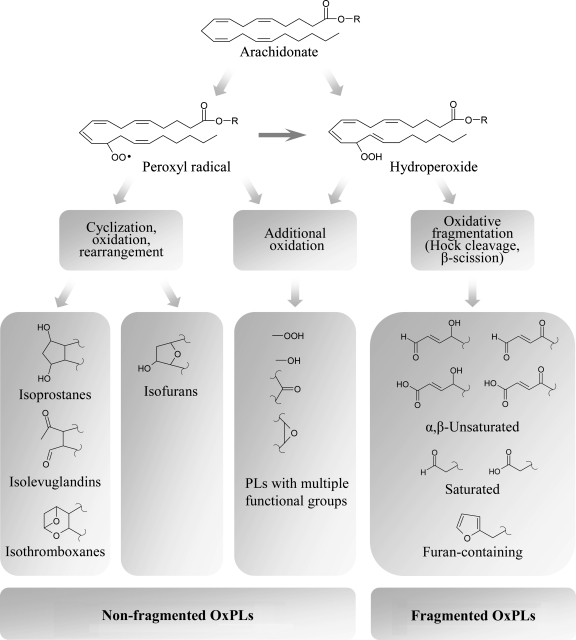
FIG. 3.
Evolution of phospholipid oxidation products. Peroxidation of PL-esterified PUFAs is initiated by formation of hydroperoxides or peroxyl radicals. Further evolution of primary PL oxidation products proceeds without participation of enzymes via three major pathways. First, additional oxidation within the same PUFA generates OxPLs with various combinations of functional groups such as hydroperoxides, hydroxides, keto- and epoxy-groups. Second pathway involves intramolecular cyclization, rearrangement, and further oxidation. If bicyclic endoperoxide is formed as an intermediate product, three groups of products are generated, including isoprostanes, isolevuglandins, and isothromboxanes, while cyclization leading to formation of monocyclic peroxide finally produces isofurans. Third group of transformations results from several chemical reactions all leading to fragmentation of PUFAs and generation of short residues having various combinations of hydroxide and carbonyl groups, or terminal furan.