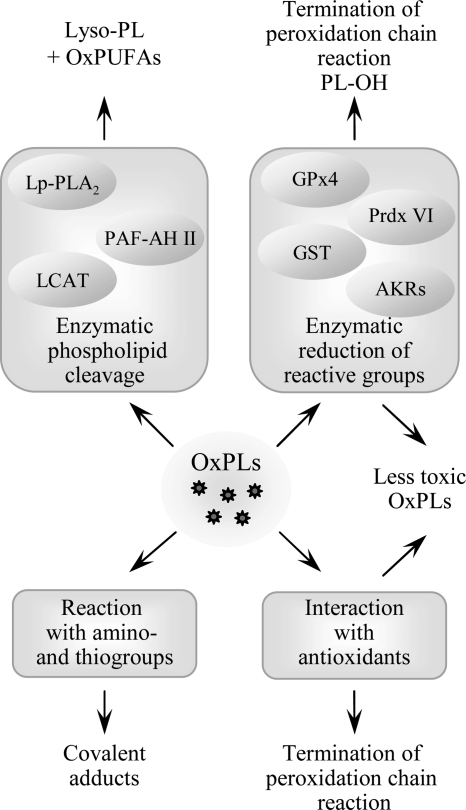
FIG. 5.
Termination of phospholipid oxidation. Several processes play a role in termination of peroxidation chain reaction and detoxification of reactive groups in PL-esterified PUFAs. In addition to scavenging of radicals by antioxidants, reactive peroxide groups are reduced by specific form of glutathione peroxidase (GPx4) capable of reducing PL-esterified residues, as well as peroxiredoxin VI and glutathione transferase (GST). Reactive carbonyl groups in PL residues are reduced by aldo-keto-reductases from AKR1A and B families. Furthermore, several phospholipases A selectively cleave oxidized residues, leading to formation of lyso-PLs and free oxidized fatty acids. Similar activity is demonstrated by LCAT. Finally, electrophilic PLs can form covalent complexes with amino acids, which may inactivate reactive groups on PLs but on the other hand can damage sensitive proteins.