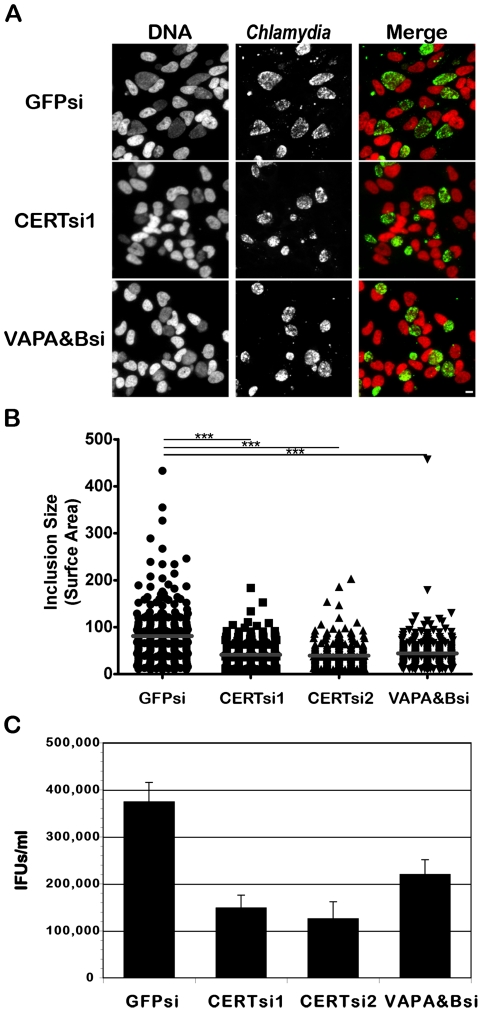
Figure 8. CERT and VAPA/B depletion impairs C. trachomatis inclusion development.
HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA (GFPsi) or two different pool of CERT siRNA (CERTsi1 and CERTsi2) or a pool of siRNA against VAPA and VAPB (VAPA&Bsi) for 3 days and infected with C. trachomatis for 32 h. (A) Immunofluorescence images to illustrate the difference in inclusion size between control (GFPsi) and CERT- (CERTsi1) or VAPA/B- (VAPA&Bsi) depleted cells. The cells were fixed and labeled with an antibody against C. trachomatis (Chlamydia, green). The DNA dye Hoechst labeled the host cell nuclei and the bacterial DNA (DNA, red). The merge images are shown on the right. Scale Bar, 10 µm. (B) For each condition, the surface area of 300 inclusions was determined. Each point represents data from a single inclusion. The grey lines indicate the mean values from the data for each condition. The difference between control and CERT or VAPA&B siRNA was statistically significant; ***P<0.0001 (Student's t test). (C) The number of infectious bacteria measured as IFUs/ml was determined 48 h p.i.. Data show the mean and standard deviation of triplicates of a representative experiment.