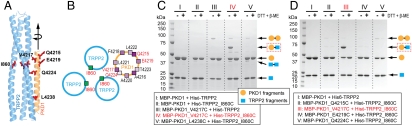
Fig. 2.
Disulfide bond analysis of a predicted close TRPP2/PKD1 contact in the docking complex. (A) The TRPP2/PKD1 coiled-coil docking complex, illustrating the side-chain positions of I860 of TRPP2 and five PKD1 residues that were individually mutated to cysteines and tested for disulfide bond formation. (B) Helical wheel representation of a portion of the TRPP2/PKD1 coiled-coil docking complex, showing the location and side-chain projection of I860 of TRPP2 and the tested PKD1 residues (red). (C and D) SDS-PAGE of various purified TRPP2/PKD1 C-terminal complexes (lanes I–V) in a reducing and nonreducing condition [with or without 100 mM DTT and 5% β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME) in a 3X SDS sample buffer]. WT protein fragments, His6–TRPP2_K695–V968 (simplified as His6–TRPP2) and MBP–PKD1_S4212–R4248 (simplified as MBP–PKD1), and their mutants, are annotated at the bottom. Putative protein composition of the major bands is indicated on the right, with the disulfide-bonded TRPP2/PKD1 complex framed with a red dashed line.