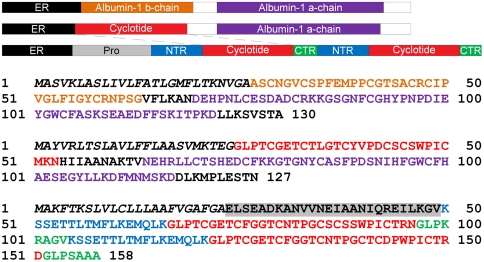
Fig. 2.
Schematic of Cter M precursor protein (middle) alongside a typical Fabaceae albumin precursor (top), and a typical two-domain cyclotide precursor (bottom). Violaceae and Rubiaceae cyclotide mRNAs encode an ER signal peptide, an N-terminal Pro region, the N-terminal repeat (NTR), the mature cyclotide domain, and a C-terminal flanking region (CTR). There may be up to three repeats of the NTR, cyclotide domain and CTR within a typical cyclotide gene. In contrast, the CterM transcript shows an ER signal peptide immediately followed by the cyclotide domain and is flanked at the C terminus by a linking peptide and the albumin a-chain. The Cter M cyclotide domain replaces the PA1b subunit-b present in typical albumin-1 genes. The sequences of the precursor proteins are illustrated (bottom) using the color scheme from the schematic representation to indicate the location of the domains.