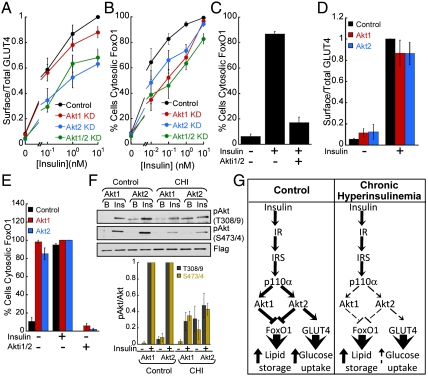
Fig. 4.
GLUT4 and FoxO1 display distinct Akt isoform requirements and sensitivities in response to insulin. (A) Insulin-dose response for surface-to-total distribution of HA-GLUT4-GFP in adipocytes treated with control or Akt isoform-specific siRNAs. Each point is the mean ± SEM, n≥3. (B) Insulin-dose response for FoxO1-GFP nuclear exclusion in adipocytes treated with control or Akt isoform-specific siRNAs. Each bar is the mean ± SEM, n≥3. (C) Effect of the Akt inhibitor Akti1/2 (1 μM) on 1 nM insulin-mediated FoxO1 nuclear exclusion. Each bar is the mean ± SEM, n = 3. (D) Surface-to-total distribution of HA-GLUT4-GFP in adipocytes overexpressing either Flag-Akt1 or Flag-Akt2 by electroporation. Each bar is the mean ± SEM, n = 3. (E) Percentage of adipocytes overexpressing either Akt1 or Akt2 by electroporation displaying cytosolic FoxO1-GFP. Flag-Akt1 and Flag-Akt2 expression was more than 10-fold higher than the endogenous kinases. 1 μM Akt inhibitor Akti1/2 for 30 min as noted. Each bar is the mean ± SEM, n = 3. (F) Immunoblot and densitometry analyses of immunoprecipitated Flag-Akt1 and Flag-Akt2. CHI: chronic hyperinsulinemia. Each point is the mean ± SEM, n = 3. (G) Schematic of insulin signaling to GLUT4 and FoxO1 in control adipocytes and adipocytes exposed to chronic hyperinsulinemia. Dashed lines indicate impaired function.