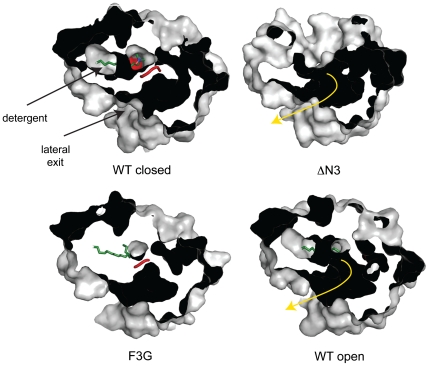
Fig. 4.
The LCFA diffusion pathway in wild-type EcFadL and mutant proteins. Shown are surface slabs viewed from the extracellular side, showing the diffusion pathway from the high-affinity binding site to the lateral opening as a dark tube. In the closed wild-type channel and in the F3G mutant, the N terminus (red) blocks the diffusion pathway. In the ΔN3 mutant and in the open wild-type channel, the diffusion pathway (shown as a yellow arrow) is uninterrupted because of the removal (ΔN3) or conformational change of the N terminus. Detergent molecules bound in the high-affinity binding sites are shown as green stick models.