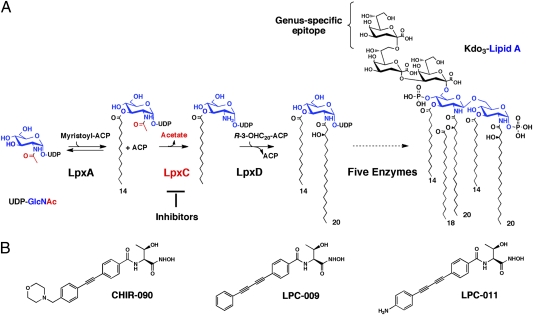
Fig. 1.
The C. trachomatis lipid A biosynthetic pathway and structures of LpxC inhibitors. (A) LOS biosynthesis begins with the acylation of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine catalyzed by LpxA, which is selective for myristoyl-ACP in C. trachomatis (42). The deacetylation of the product UDP-3-O-(myristoyl)-N-acetylglucosamine in C. trachomatis, catalyzed by LpxC, is considered the first committed and irreversible step (16). The relatively simple structure of the major species of C. trachomatis LOS, consisting of Kdo3-lipid A, is well characterized (6). The C. trachomatis genus-specific epitope (i.e., the additional outer Kdo residue not present in other bacteria) is recognized by anti-C. trachomatis LOS antibodies. (B) Structures of the LpxC inhibitors CHIR-090, LPC-009, and LPC-011.