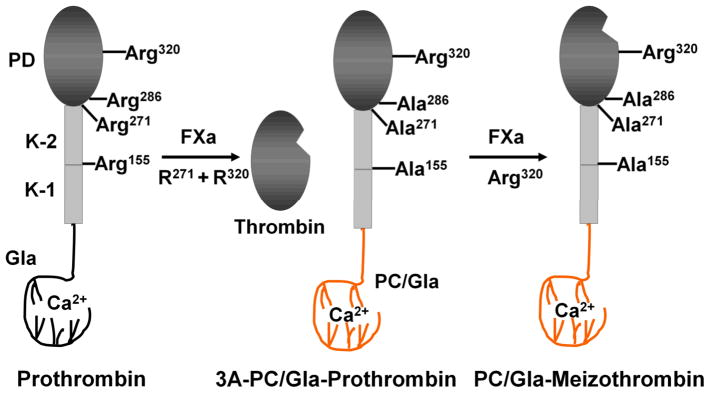
Fig. 1.
Cartoons of construction and factor Xa activation of wild-type and the three Arg to Ala substitution mutants of prothrombin. (Left Panel) The proteolytic cleavage of wild-type prothrombin by factor Xa after Arg-320 generates an intermediate active product called meizothrombin. A second cleavage at Arg-271 by factor Xa separates the catalytic domain of prothrombin from the non-catalytic Gla, Kringle-1 and Kringle-2 domains to yield thrombin. Further cleavages at Arg-155 and Arg-286 can occur by a feed-back cleavage mechanism by both thrombin and meizothrombin. (Central Panel) A prothrombin derivative (3A-PC/Gla-prothrombin) was prepared in which the Gla-domain of the molecule was replaced with the corresponding domain of protein C and its Arg-155, Arg-271 and Arg-286 residues were substituted with 3 Ala residues. (Right Panel) The prothrombin chimeric mutant can be activated by factor Xa through cleavage after Arg-320 to yield the active protease PC/Gla-meizothrombin. K-1 and K-2 represent Kringle-1 and 2 domains of prothrombin, respectively. PD, protease domain. The figure is adopted from Ref. 19 with modifications.