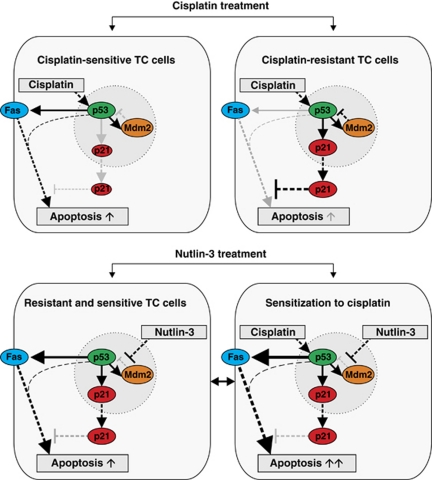
Figure 7.
Simplified model showing the role of the MDM2/p53 axis in regulating the sensitivity to cisplatin and Nutlin-3 in wild-type p53-expressing TC cells. P53 is a transcriptional activator of p21, Fas and MDM2. Cisplatin sensitive TC cells have low levels of p21 and cisplatin-resistant TC cells, due to higher CDKN1A expression levels and lower levels of Oct4 and miR-106b family members, high levels of cytoplasmic p21, which is a key determinant of resistance to cisplatin-induced apoptosis.19 Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in TC cells also involves activation of the Fas death receptor pathway via elevated Fas membrane expression. High cytoplasmic p21 levels inhibit Fas death receptor-mediated apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant TC cells.30 Moreover, cisplatin-induced DNA damage activates p53 and enhances release of p53 from MDM2–p53 complex, while sustained MDM2–p53 complex formation is found in cisplatin-resistant cells. Interfering in MDM2–p53 complex formation by Nutlin-3 treatment (or suppression of MDM2) substantially induces Fas expression, resulting in apoptosis of both cisplatin sensitive and resistant TC cells. Cisplatin in combination with Nutlin-3 further enhances Fas expression and sensitises cisplatin-sensitive and resistant TC cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Dotted lines indicate interaction or signaling. Solid lines indicate p53-dependent transcription. Grey dotted and solid lines specify reduced activity