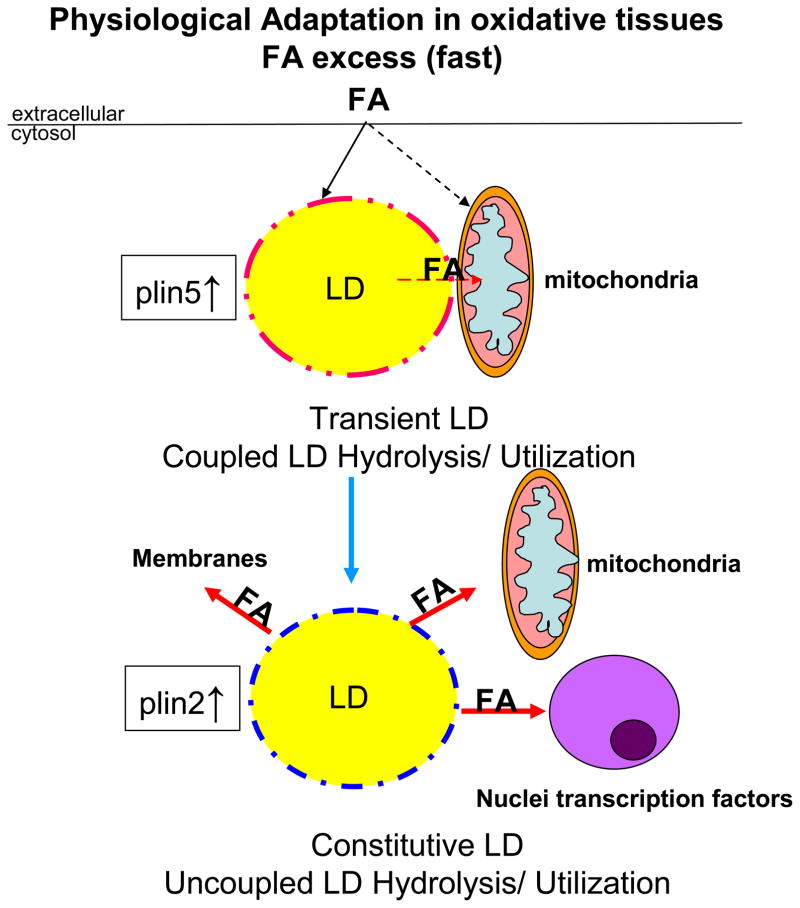
Figure 3. Hypothetical model of the role of perilipin 5 in cellular lipid homeostasis in adaptive response to excess FA flux in oxidative cells under physiological conditions.
During fasting conditions, adipose tissue lipolysis provides FA fuel to other organs. Excess FA supply to liver or heart leads to a rapid increase in LD biogenesis. Based on present studies, it can be hypothesized that perilipin 5, already present in the cytosol, is rapidly recruited to the surface of a nascent pool of LDs and regulates LD TAG hydrolysis, being a novel protein kinase A (PKA) downstream target, by modifications in its scaffolding properties for ATGL and CGI-58, controlling FA utilization through recruitment of mitochondria to LDs by its C-terminal domain and finally protecting mitochondria against lipotoxicity. Perilipin 2 coats a pool of constitutive droplets which are not coupled to specific use.