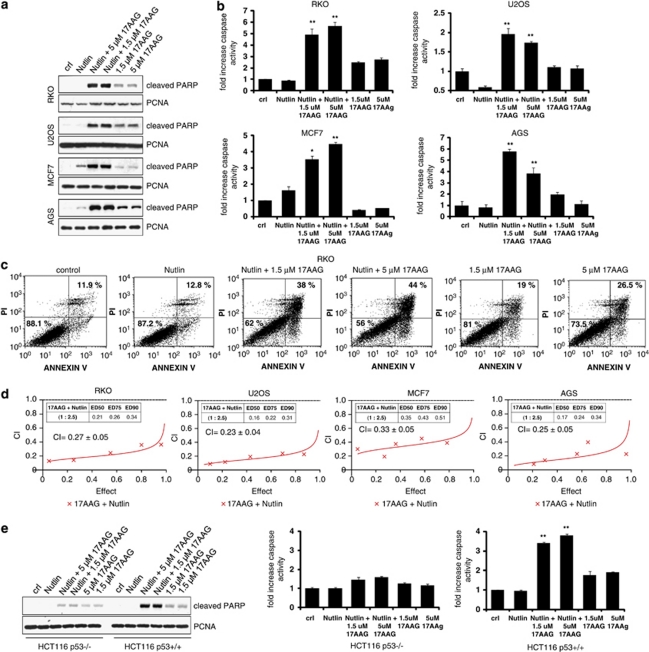
Figure 3.
17AAG synergizes with Nutlin to induce apoptosis in a p53-dependent manner. (a) Combined treatment of 17AAG and Nutlin significantly increases PARP cleavage compared with each single treatment. RKO, U2OS, MCF7 and AGS cells were pretreated with 1.5 or 5 μM of 17AAG for 1 h, followed by 10 μM of Nutlin for an additional 24 h where indicated. Treatment with 17AAG alone was for 24 h. Controls received no treatment. PARP cleavage was analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody that only recognizes cleaved PARP. PCNA is a loading control. (b) Increase of caspase activity upon combined treatment. The indicated cell lines were treated as shown in panel a and caspase activity was measured. The error bars represent standard errors from four replicates. * denotes P<0.05; ** denotes P<0.005 comparing Nutlin to Nutlin+17AAG. (c) Increase of cell death upon combined treatment. RKO cells were treated as above and measured by FACS for Annexin-V and PI staining. % survival (Annexin-V/PI double-negative population) is indicated in the lower left quadrant and total % death is indicated in the upper right quadrant. (d) Synergistic induction of cell death by Nutlin+17AAG. The indicated cell lines were treated with increasing doses of 17AAG or Nutlin alone or with combinations at a fixed ratio for 72 h. The % of dead cells was determined by trypan blue exclusion assays. CIs were calculated by the isobologram analysis using the CalcuSyn software.27 (e) The combination of Nutlin+17AAG increases cell death in p53+/+ but not in p53−/− cells. HCT116 p53+/+ or p53−/− cells were treated as shown in panel a. PARP cleavage (left) and caspase activity (right) were analyzed. The error bars represent standard errors from four replicates. **denotes P<0.005 comparing Nutlin to Nutlin+17AAG