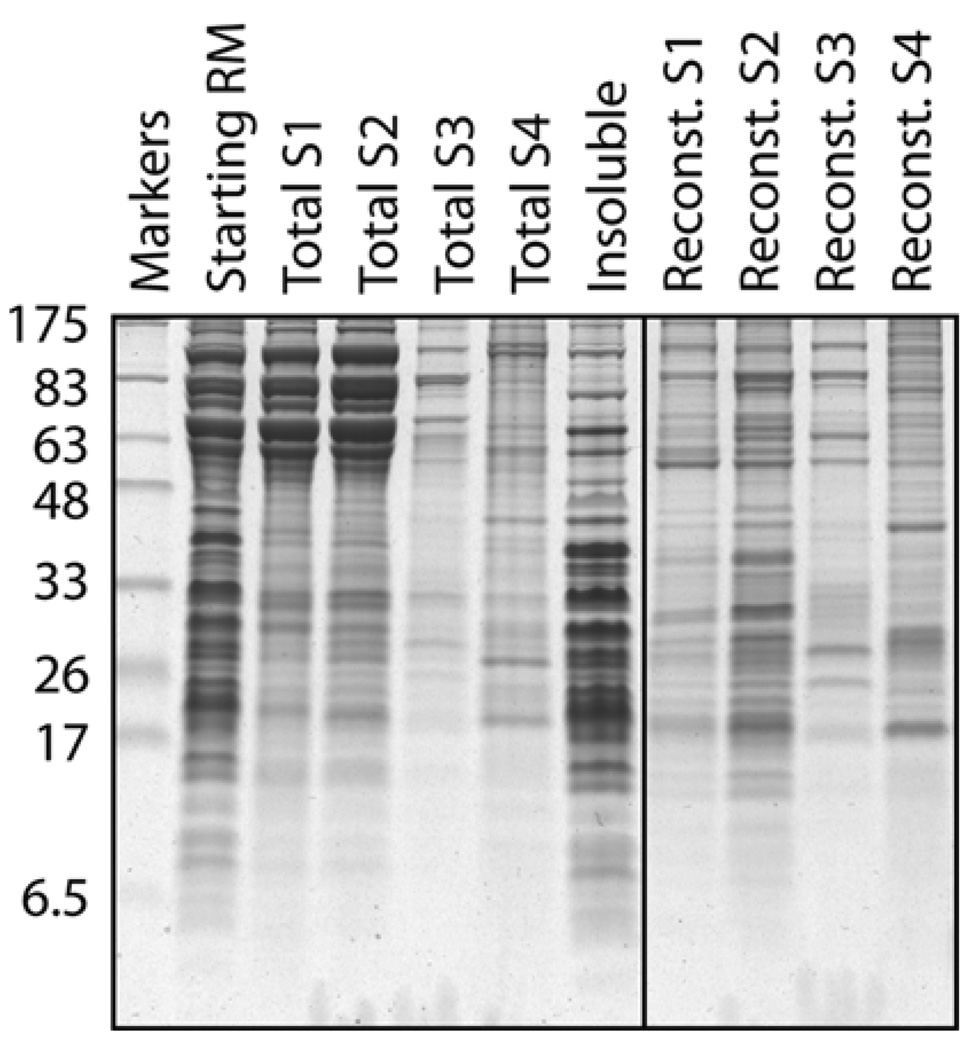
Fig. 20.4.
Example of differential solubilization and reconstitution of membrane proteins. Crude RMs (lane 1) were sequentially extracted by four buffers containing different amounts of detergent and salt to generate four supernatant fractions (S1–S4) and an insoluble pellet (primarily containing ribosomes). Each of these four fractions was then reconstituted in the presence of phospholipids by detergent removal, and the resulting proteoliposomes were also analyzed on the gel. Note that the very abundant high molecular weight proteins in S1 and S2 (primarily lumenal proteins) are not reconstituted. Note also the different protein profiles of the different proteoliposomes illustrating the utility of differential membrane protein extraction as a purification step. The detergent in this case was DeoxyBigCHAP, although similar results can be obtained with other detergents.