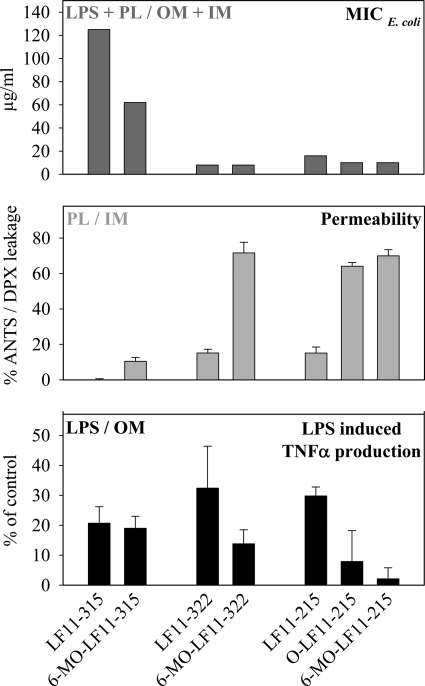
FIGURE 7.
Correlation of MICE. coli with membrane permeabilization and LPS neutralization of nonacylated peptides and their N-acylated derivatives (OM, outer membrane; IM, inner membrane; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; PL, phospholipids). Top panel, MICE. coli values (taken from Table 1) reflecting the interaction of peptides with both LPS and phospholipids. Middle panel, interaction of peptides with phospholipids as deduced from membrane permeability measurements of ANTS/DPX leakage from LUVs of E. coli membrane lipids (50 μm) in the presence of 4 μm peptide at 37 °C (see also Fig. 5). Bottom panel, interaction of peptides with LPS as illustrated from LPS Ra (S. minnesota R60) induced TNFα production in human mononuclear cells at 1 ng/ml and its inhibition by nonacylated and N-acylated peptides. Values are given as a percentage of control.