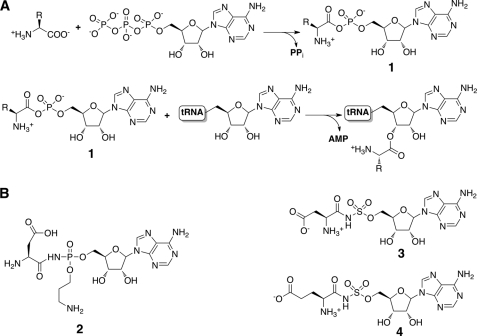
FIGURE 1.
tRNA synthetase mechanism and structures of inhibitors. A, the two-step reaction for the esterification of a specific amino acid onto its cognate tRNA to form a charged aminoacyl-tRNA proceeds through the production of a hydrolytically labile aminoacyl adenylate (compound 1). B, chemical structures of synthetic and naturally occurring aminoacyl adenylate mimics, including McC (compound 2), DSA (compound 3), and ESA (compound 4).