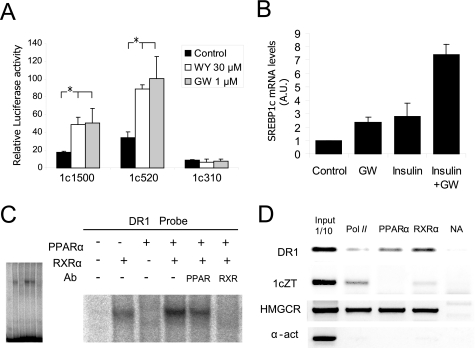
FIGURE 4.
PPARα regulates human SREBP1c promoter activity. A, PPARα-dependent regulation of the SREBP1c promoter was analyzed by luciferase assays using the −1564/+1-luc (1c1500), −520/+1-luc (1c520), and −310/+1-luc (1c310) constructs in the presence of WY14643 (WY) or GW7647 (GW) as selective PPARα agonists. Activities of the promoter constructs transfected in rat primary hepatocytes under basal conditions (black bars), 30 μm WY14643 (white bars) or 1 μm GW7647 (gray bars) are shown. The results represent relative Firefly/Renilla luciferase activities considering the wild-type construct under basal conditions as the reference value. Values are the mean ± S.E. of four separate experiments. *, p < 0.05. B, the endogenous SREBP1c expression in cultured human hepatocytes was analyzed by quantitative PCR. Cells were seeded under basal conditions (control) or treated with 1 μm GW7647 (GW) and/or 100 nm insulin. Total RNA was extracted 24 h after treatment, and cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcriptase. The relative amount of the SREBP1c/36B4 expression was determined in each condition by taking the basal condition as the reference value. The results are the mean ± S.E. of three separate experiments. Differences between the control and the treatments were statistically significant. C, analysis of PPAR binding in vitro to the SREBP1c promoter. EMSA was performed with recombinant human proteins incubated with 32P-labeled oligonucletide encoding for the DR1 element of the human SREBP1c promoter. α-PPAR α or α-RXR α antibodies were used for the supershift assays. The complete EMSA gel (left panel) shows that an equal amount of the probe was loaded in all the lanes. D, analysis in vivo of PPAR binding to the SREBP1c promoter. The ChIP assay was performed in human hepatocytes treated with 1 μm GW7647. Immunoprecipitation of samples was performed with the α-PPARα antibody. A positive control of transcriptionally active genes was performed using the α-RNA pol II antibody and a negative control with no antibody. An α-RXR antibody was used as a positive control for the PPARα activated promoters. An analysis of the HMGCR promoter was used as a positive control for PPARα and RXR binding. The α-actin primers were used as negative control for all the antibodies. The results are representative of the PCR fragments analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis of two independent experiments.