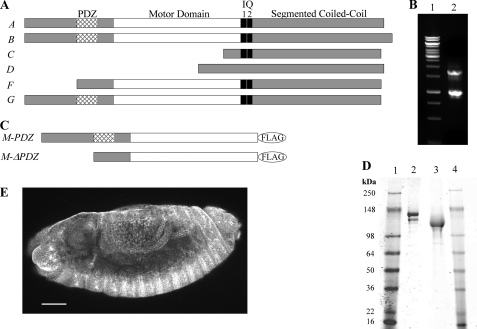
FIGURE 1.
Sequence analysis of PDZ and ΔPDZ isoforms of Drosophila myosin-18. A, sequence analysis of 17 exons in the Drosophila myosin-18 gene (CG31045) was performed using the ClustalW multiple alignment algorithm. The domain analysis using Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (SMART) at European Molecular Biology Laboratory was aligned with exons to illustrate six alternatively spliced isoforms (A–G) varying at the N terminus. B, lane 1 is molecular weight standards. Lane 2, 5′ RACE analysis of whole fly mRNA using nested PCR to amplify PDZ and ΔPDZ isoforms yielded two bands, one at 1.7 kb corresponding to PDZ-containing isoforms and one at 0.9 kb corresponding to the ΔPDZ isoform. C, expression constructs of minimal motors of Drosophila myosin-18 for baculoviral expression in Sf9 cells truncate the sequence at Leu1319 for M-PDZ and Leu1082 for M-ΔPDZ, the residues corresponding to Dictyostelium myosin-2 Arg761, followed by a C-terminal FLAG tag for purification. D, M-PDZ and M-ΔPDZ expressed proteins purified using a FLAG affinity tag and fractionated by 4–20% Tris-glycine SDS-PAGE. Lane 1, molecular weight markers; lane 2, M-PDZ at 140 kDa; lane 3, M-ΔPDZ at 116 kDa: lane 4, molecular weight markers. E, representative Drosophila embryo (stage 13) stained with a polyclonal antibody at a 1:1,000 dilution in blocking buffer (scale bar, 50 μm). The primary antibody was raised in rabbit against an uninterrupted segment of the coiled coil region of myosin-18 that is shared between all six potential isoforms of the protein. Visualization of the localization pattern used Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody at a 1:5,000 dilution in blocking buffer. Using confocal microscopy with a 20×, 0.75 numerical aperture oil immersion objective and a section depth of 1.2 μm, the localization of myosin-18 was ubiquitous throughout all embryonic tissues as seen in this projection of 17 confocal sections. Such ubiquitous staining was seen throughout all observed embryonic developmental stages.