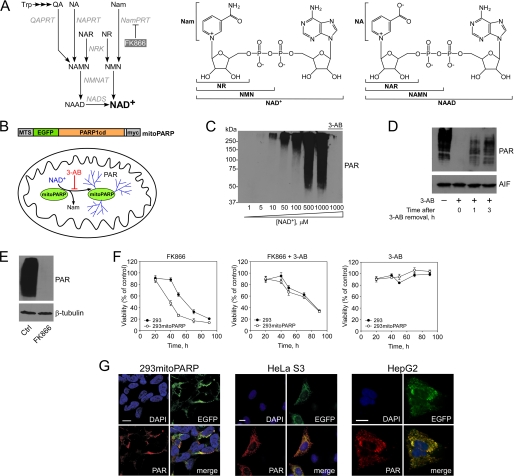
FIGURE 1.
Targeted expression of the catalytic domain of PARP1 as sensor for mitochondrial NAD+ levels. A, overview of NAD+ biosynthesis in humans. NAD+ can be synthesized from pyridine bases or nucleosides, which are initially converted to mononucleotides. The tryptophan (Trp) degradation product quinolinic acid (QA) is transformed to nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NAMN) by quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase (QAPRT). Nicotinamide (Nam) and nicotinic acid (NA) are converted to the corresponding mononucleotides (NMN and NAMN) by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NamPRT) and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase (NAPRT), respectively. FK866 inhibits NamPRT. NMN and NAMN are also generated through phosphorylation of nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinic acid riboside (NAR), respectively, by nicotinamide riboside kinase (NRK) activity. NAMN and NMN are converted to the corresponding dinucleotide (NAAD or NAD+) by NMN adenylyltransferase (NMNAT). NAD synthetase (NADS) amidates NAAD to NAD+. The two right panels indicate the structures of NAD+ and its metabolites. B, experimental system to monitor mitochondrial NAD+ levels. mitoPARP automodifies itself, and its activity is inhibited by 3-AB. Generation and functional verification of the mitoPARP construct have been described (36). MTS, mitochondrial targeting sequence. C, PAR accumulation depends on the NAD+ concentration. The Western blot shows automodification of purified, recombinant PARP1cd (overexpressed in E. coli) after incubation with the indicated concentrations of NAD+. The smear reflects the heterogeneity of polymer lengths. D, 293mitoPARP cells constitutively contain PAR in mitochondria (left lane). Incubation with 3-AB for 24 h diminishes the PAR signal (2nd lane). Following washout of 3-AB, polymers accumulate over time. E, decrease of mitochondrial NAD+ by NamPRT inhibition. Relative NAD+ content in mitochondria was detected in lysates of 293mitoPARP cells treated or not (Ctrl) with FK866 for 24 h. F, mitoPARP activity increases the sensitivity toward NamPRT inhibition. Parental 293 and 293mitoPARP cells were treated with FK866 or 3-AB as indicated. G, mitoPARP (detected by its enhanced GFP(EGFP) portion) leads to mitochondrial PAR accumulation when stably (293mitoPARP) or transiently (HeLa S3 and HepG2) expressed. Bar, 10 μm.