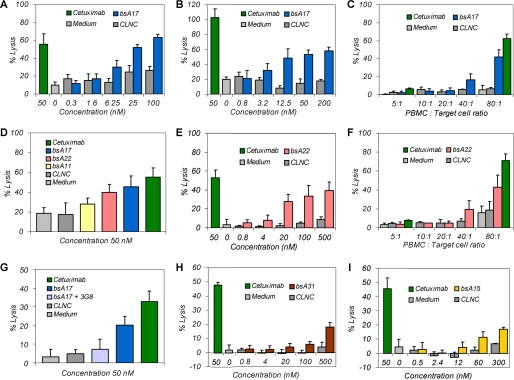
FIGURE 6.
Functional ADCC assays of bi-specific aptamers. A, bi-specific aptamer bsA17-mediated specific GTL-16 cell lysis as compared with background levels of non-binding negative control aptamer (CLNC) and reference with medium only. B, similar bsA17-mediated concentration-dependent specific EBC-1 cell lysis. C, PBMC:target cell ratio reduction diminished cytotoxicity of both bsA17 and cetuximab at 50 nm. D, influence of linker lengths on bsA-mediated cell lysis. Estimated linker lengths were 49 Å for bsA17, 105 Å for bsA22 and 217 Å for bsA11. E and F, bsA22-induced specific cytotoxicity dependent on aptamer concentration and effector cell amount. G, the addition of 20-fold molar excess of antibody 3G8 resulted in a decrease of bsA17-mediated lysis due to inhibition of bsA17-binding to CD16α. H, bsA31 with lower c-Met affinity induced weaker but distinct lysis at higher concentrations. I, bsA15, composed of CLN0123 as a lower affinity CD16α binding entity, mediated weak but significant cytotoxicity as well. GTL-16 cells were applied in all measurements, except for B. Maximal lysis varied between individual experiments due to donor and CD16α allotype dependence. ADCC assays were performed 5 times with n = 4 (A), 4 times with n = 4 (B), 3 times with n = 3 (C), 3 times with n = 9 (D), 4 times with n = 4 (E), 1 time with n = 3 (F), 3 times with n = 9 (G), 2 times with n = 4 (H), and 1 time with n = 4 (I), and representative measurements are shown as mean ± S.D.