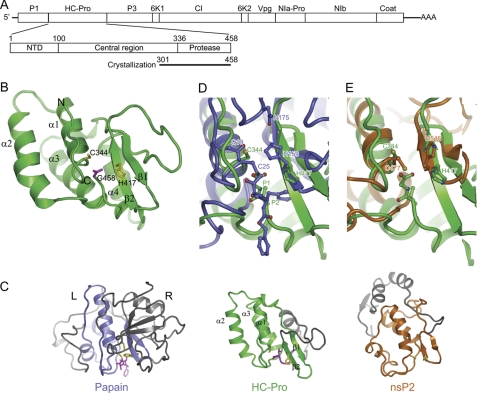
FIGURE 1.
Structure of HC-Pro CPD from TuMV. A, diagram of the TuMV RNA genome, the domain organization of HC-Pro, and the construct used for crystallization. Mature products for the polyprotein are indicated. B, ribbon representation of the CPD structure. The secondary structural elements and the N and C terminus are indicated. The catalytic dyad residues Cys344 and His417 (yellow) and the C-terminal residue Gly458 (magenta) are shown as sticks. C, structural comparison of HC-Pro CPD, papain (Protein Data Bank ID code 6PAD), and nsP2 CPD of Venezuelan equine encephalitis alphavirus (Protein Data Bank ID code 2HWK). The three structures are aligned around the catalytic dyad residues. The equivalent structure elements are colored green in HC-Pro, blue in papain, and orange in nsP2, whereas the rest of the structures are gray. The catalytic residues and substrate/inhibitor are shown in sticks and are colored in yellow and magenta, respectively. D and E, superposition of the active site of HC-Pro CPD with that of papain covalently linked to an inhibitor (D) and nsP2 (E).