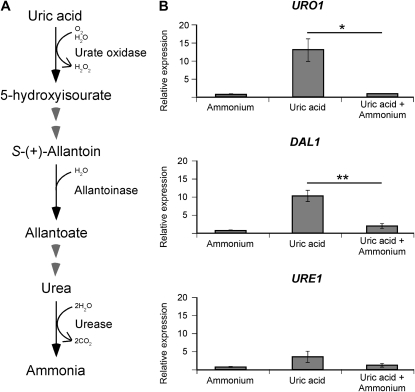
Figure 1.—
The predicted catabolic enzyme-encoding genes of uric acid, URO1 and DAL1, are sensitive to nitrogen metabolite repression. (A) Scheme representing the predicted (partial) uric acid degradation pathway of C. neoformans. (B) cDNA from wild-type H99 grown in YNB supplemented with ammonium, uric acid, or uric acid plus ammonium (10 mm each nitrogen source) were amplified via qRT-PCR using primers against URO1 (urate oxidase), DAL1 (allantoinase), URE1 (urease), and the control gene ACT1 (actin). In the presence of uric acid as the sole nitrogen source, the expression of URO1 and DAL1 was significantly increased while that of URE1 was slightly increased, but this upregulation was abolished when ammonium was also present. This nitrogen metabolite repression sensitivity of URO1 (* denotes P < 0.05) and DAL1 (** denotes P < 0.01) was statistically significant. Error bars represent standard errors across three biological replicates.