Figure 4.
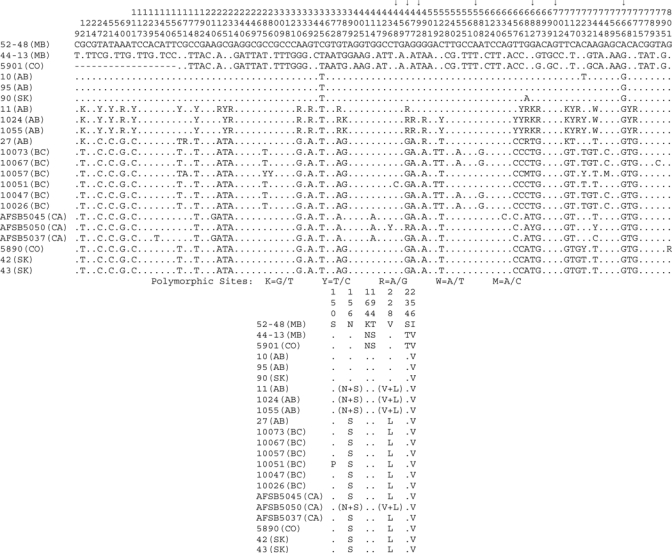
Nucleotide and amino acid variations among Calbertado virus nonstructural protein 5 (NS5) gene sequences. Nucleotide and protein alignments were generated for NS5 sequences, and resulting alignments were condensed to depict only the positions found to be variable between the pools. Alignment coordinates are indicated vertically above each position. Alignment summaries are relative to the 52-48 (MB) sequence, positions found to be identical are represented with a dot, and gaps are indicated with a dash. Variations are indicated with the substitution identified at that location. Standard International Union of Biochemistry coding was used in the nucleotide alignment for positions found to be polymorphic (K = G/T, Y = T/C, R = A/G, W = A/T, M = A/C). Even with the extensive nucleotide variations noted in this region, which codes for 270 amino acids of NS5, only 7 amino acid positions were found to differ between various sequences (nucleotide substitutions responsible for these changes are indicated by arrows). A summary of these amino acid substitutions and positions is included below the nucleotide alignment. Several of the reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction products sequenced were found to contain polymorphic sites, indicating that the mosquito pool contained a mixture of viruses. Two of these polymorphic sites occurred in codon-altering positions as noted in the amino acid summary.
