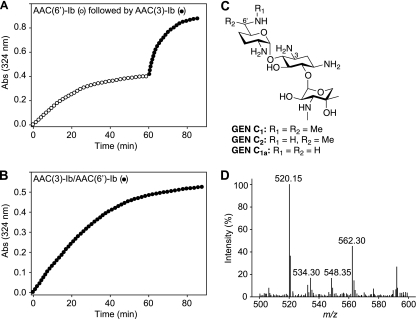
Fig. 4.
(A) Spectrophotometric assay demonstrating the diacetylation of GEN via sequential reactions using the individual components AAC(6′)-Ib′ (open circles) and AAC(3)-Ib (filled circles) from the bifunctional enzyme AAC(3)-Ib/AAC(6′)-Ib′. (B) Spectrophotometric assay demonstrating the diacetylation of GEN using the bifunctional enzyme AAC(3)-Ib/AAC(6′)-Ib′ (filled circles). (C) Structures of GEN C1, GEN C2, and GEN C1a. (D) Mass spectra for the reaction of GEN with acetyl-CoA using the bifunctional enzyme AAC(3)-Ib/AAC(6′)-Ib′, showing the production of N-acetyl-GEN C1 (m/z 520.15), N,N′-diacetyl-GEN C1a (m/z 534.30), N,N′-diacetyl-GEN C2 (m/z 548.35), and N,N′-diacetyl-GEN C1 (m/z 562.30). The same masses were observed when AAC(6′)-Ib′ and AAC(3)-Ib were used sequentially.