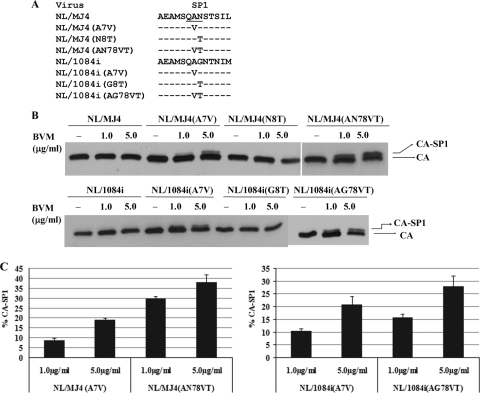
Fig. 3.
Importance of SP1 residues 7 and 8 in the modulation of BVM activity in inhibiting the conversion of the capsid precursor, CA-SP1, to mature capsid protein. (A) Panel of Gag SP1 chimeras constructed between NL4-3 and MJ4 or between NL4-3 and 1084i and containing various mutations targeting the SP1 polymorphism motif (underlined). Dashes represent residues that are identical to the parental virus (NL/MJ4 or NL/1084i) sequence. (B) COS-1 cells were transfected with the indicated mutant proviral DNAs as described in the legend to Fig. 1. BVM or DMSO (no-drug control) was maintained throughout the period of the culture, and SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis of viral proteins obtained from the cultures were performed as described in the legend to Fig. 1. (C) Protein bands were analyzed by ImageJ software (http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/) to quantify the percentage of CA-SP1 relative to total CA-SP1 plus CA. All data shown are means and standard deviations for three independent experiments performed in duplicate.