Fig. 1.
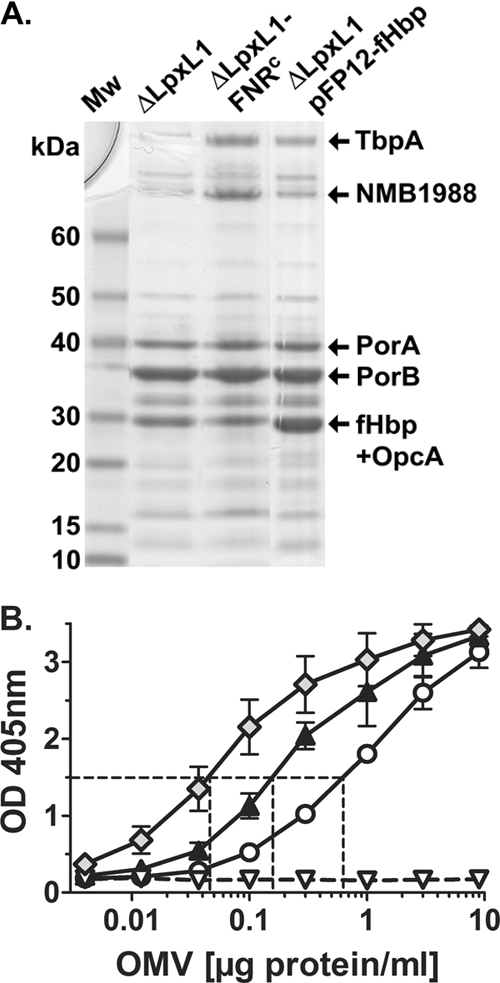
Characterization of NOMV vaccines. (A) SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining of NOMVs prepared from recombinant H44/76 strains (Table 1). The NOMVs from the recombinant ΔLpxL1-FNRc strain had larger amounts of two high-molecular-mass proteins, which in parallel experiments were identified by mass spectrometry as transferrin binding protein A and NMB1988 (9, 37). The NOMVs from the recombinant ΔLpxL1-pFP12-fHbp strain showed larger amounts of a band resolving at ∼30 kDa. In parallel experiments the band resolving in this portion of the gel for NOMV preparations from both the ΔLpxL1-FNRc and ΔLpxL1-pFP12-fHbp recombinant strains contained fHbp and OpcA. (B) Relative amounts of fHbp in NOMV vaccines prepared from recombinant H44/76 strains as measured by a capture ELISA. Circles, ΔLpxL1; black triangles, ΔLpxL1-FNRc; Diamonds, ΔLpxL1-pFP12-fHbp; white triangles, ΔLpxL1ΔfHbp. The NOMV vaccines from the recombinant strains ΔLpxL1-FNRc and ΔLpxL1-pFP12-fHbp contained ∼3- and 10-fold more fHbp, respectively, than the NOMVs from the ΔLpxL1 recombinant strain with wild-type fHbp expression.
