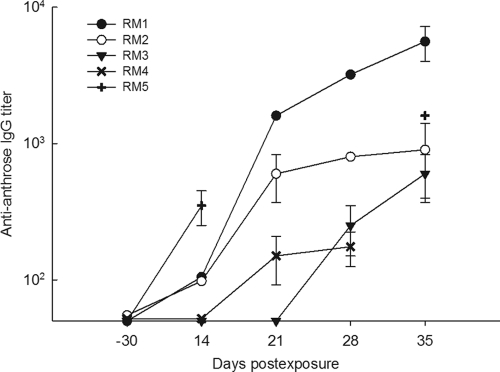
Fig. 2.
Anti-ATS IgG responses in rhesus macaques (RM) that survived inhalation anthrax. Animals were exposed to 246 ± 40 LD50 equivalents of B. anthracis Ames spores. Animal RM1 was an untreated control. Two of the animals (RM2 and RM3) were treated with ciprofloxacin starting at 48 h. Animals RM4 and RM5 received ciprofloxacin starting at 72 h postexposure. Anti-ATS IgG was determined by ELISA. Error bars indicate the standard deviations of four titer determinations based on OD measurements from two separate experiments.