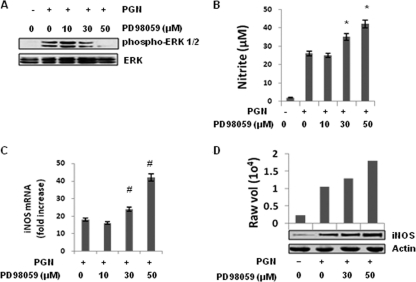
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of MEK1-ERK by PD98059 augmented iNOS expression and NO production induced by PGN. Mouse peritoneal macrophages were treated with or without various concentrations of PD98059 (10, 30, or 50 μM) for 30 min, washed, and then further treated with PGN (10 μg/ml) for 30 min, 6 h, or 18 h. (A) After 30 min, the phosphorylation of ERK was determined by immunoblotting cell lysates with antibody specific for a phospho-ERK (p-p42 and p-p44). The bottom panel shows an immunoblot with an antibody to ERK2. (B) After 18 h, the NO production in culture supernatants of mouse peritoneal macrophages was evaluated by using a Griess reagent assay. Each bar represents the standard error of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 compared to PGN. (C) After 6 h, the RNA was isolated and checked for iNOS transcripts by real-time RT-PCR. Each bar represents the fold expression relative to untreated macrophages. The data represent the means ± the SD of three independent experiments. #, P < 0.01 compared to control macrophages. (D) After 18 h, the macrophages were lysed, and cell lysates were immunoblotted with a polyclonal anti-iNOS antibody. The same blot was reprobed with anti-actin antibody to demonstrate equal protein loading.