Fig. 1.
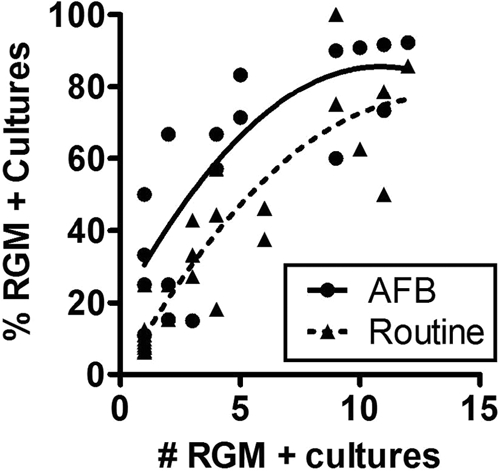
Comparison of positivity rates for routine and AFB cultures. The relationship between the number of RGM-positive cultures and the percentage of RGM-positive cultures was examined, with the assumption that the percentage of RGM-positive cultures of samples from patients with high numbers of positive cultures (suggesting persistent infection) would provide an estimate of sensitivity. Curve fitting suggested that the percentages of positive cultures plateaued at ∼85% for AFB cultures and ∼75% for routine cultures when the total number of RGM-positive cultures was ≥9.
