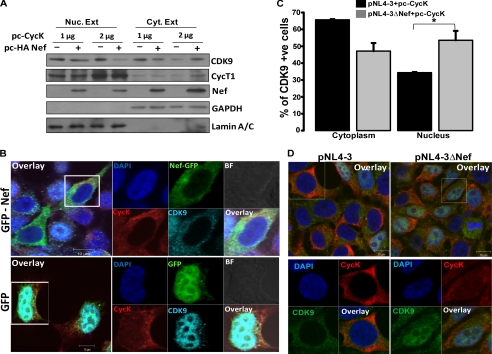
FIGURE 7.
Cyclin K restricts CDK9 nuclear translocation in presence of Nef. A, Cyclin K and Nef overexpression restricts CDK9 from nuclear translocation. HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with increasing amounts of pc-CycK with or without HA-Nef expression vector as indicated in the figure. Equal amounts of nuclear (Nuc. Ext) and cytoplasmic extracts (Cyt. Ext) were used for immunoblotting with CDK9, CycT1, and Nef antibodies as described in the text. The same blot was probed for Lamin A/C and GAPDH to serve as loading controls. B, Cyclin K and Nef overexpression inhibits CDK9 nuclear translocation as visualized by immunofluorescence. HEK-293T cells were grown on a coverslip and co-transfected with pc-CycK and EGFP-Nef or EGFP control vectors. After 24 h, cells were stained for CycK and CDK9 as described in the text. Cells were then mounted onto a glass slide and visualized by a confocal microscope. C, CDK9 translocation into the nucleus is increased in the cells transfected with the Nef-deleted molecular clone. HEK-293T cells were grown on a coverslip and were transfected with pNL4-3 or pNL4-3ΔNef along with pc-CycK. Immunofluorescence staining was performed with CDK9 and CycK antibodies. Cells stained for CDK9 in the nucleus or cytoplasm were counted and plotted as a bar diagram with data from three independent experiments. Black and gray bars indicate CDK9-stained cells transfected with pNL4-3 and pNL4-3ΔNef, respectively. D, representative immunofluorescence images of CDK9 localization in the experiment described in C. Left and right panels are immunofluorescence images of cells transfected with pNL4-3 and pNL4-3ΔNef along with pc-CycK, respectively. BF, bright field; +ve, positive.