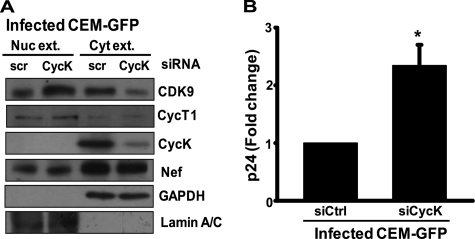
FIGURE 8.
Cyclin K silencing leads to increased CDK9 nuclear translocation and virus production in HIV-1-infected CEM-GFP T-cells. A, Cyclin K down-regulation leads to increased CDK9 translocation into the nucleus of HIV-1-infected T cells. CEM-GFP cells were transfected with 200 nm control (siCtrl) and CycK-specific siRNA (siCycK). 24 h post-transfection, cells were infected with HIV-1NL4-3 at 0.5 multiplicity of infection; on day 3, cells were harvested; and nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were prepared as mentioned under “Experimental Procedures.” Equal amounts of extracts were used for immunoblotting with CDK9, CycT1, CycK, and Nef antibodies. GAPDH and Lamin A/C were used as loading controls. B, Cyclin K down-regulation leads to increased virus production from HIV-1-infected T-cells. The amount of virus present in the culture supernatant of the cells described in A was estimated by a p24 antigen capture ELISA. Nuc. Ext, nuclear extract; Cyt. Ext, cytoplasmic extract; scr, scrambled.