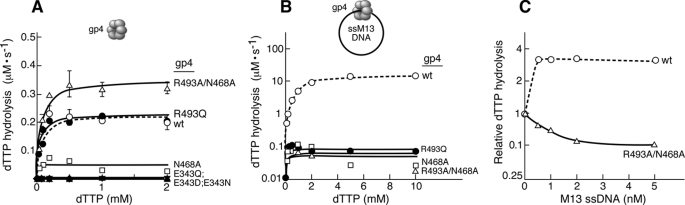
FIGURE 2.
dTTP hydrolysis activity in the absence and presence of ssDNA. dTTP hydrolysis assays were performed in 10-μl reactions containing the indicated concentrations of [α-32P]dTTP, 100 nm of either wild-type or altered gp4, and 1 nm circular M13 ssDNA where indicated. After incubation at 37 °C for 30 min, EDTA was added to stop the reaction. The reaction was spotted on TLC plates coated with polyethyleneimine and dTDP was separated from dTTP in a buffer containing 0.5 m LiCl2 and 0.5 m formic acid. The quantity of dTTP hydrolysis was calculated by measuring the intensities corresponding to [α-32P]dTDP and unhydrolyzed [α-32P]dTTP. Reaction kinetics was derived with the help of Michaelis-Menten equation in GraphPad Prism software and presented in Table 2. A, dTTP hydrolysis in the absence of ssDNA. B, dTTP hydrolysis in the presence of 1 nm M13 ssDNA. The values in the y axis are in log10 scale. Note that 1 nm M13 ssDNA could stimulate the rate of dTTP hydrolysis by wild-type gp4 up to 100-fold. C, effect of M13 ssDNA on dTTP hydrolysis catalyzed by gp4-R493A/N468A compared with wild-type gp4. The assays were carried out as described above, except that different concentrations of M13 ssDNA (0–5 nm) were added to the reactions containing 200 μm [α-32P]dTTP. The rate of dTTP hydrolysis by gp4-R493A/N468A (0.35 μm/s) and wild-type gp4 (0.22 μm/s) in the absence of M13 ssDNA were normalized to 1. The rates of dTTP hydrolysis in the presence of different concentrations of the M13 ssDNA were converted relative to the corresponding protein activity in the absence of DNA. Please note that in all cases less than 30% of the dTTP is hydrolyzed in 30 min for each of the concentrations examined.