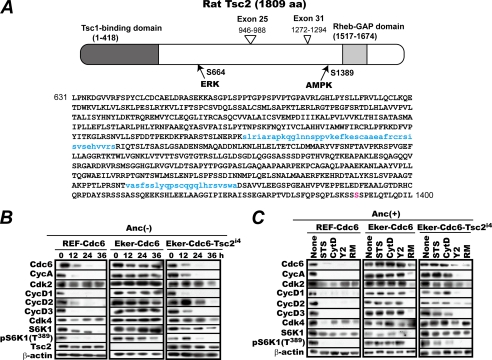
FIGURE 2.
A, schematic presentation of rat TSC2i4 generated by alternative splicing that removes exons 25 and 31. The two stretches of amino acids encoded by exons 25 and 31, which are absent in TSC2i4, are shown in lowercase blue letters. The amino acid (aa) numbers in the figure refer to full-size TSC2. The amino acid in red is the AMP-dependent kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation site (35). GAP, GTPase-activating protein. B, complementation with Tsc2i4 restores the susceptibility of Eker-Cdc6 cells to anchorage deprivation. Rapidly proliferating REF-Cdc6, Eker-Cdc6, and Eker-Cdc6 cells complemented with Tsc2i4 (Eker-Cdc6-Tsc2i4) were cultured in methylcellulose medium with cell sampling every 12 h for 36 h. The harvested cells were analyzed for the indicated factors by immunoblotting. C, complementation with Tsc2i4 restores the susceptibility of Eker-Cdc6 cells to Y2 but not to staurosporine or cytochalasin D. The same set of cells proliferating on culture dishes were treated with or without RM, STS, CytD, or Y2 for 24 h in the presence of Z-VAD as in Fig. 1A and analyzed for the indicated factors by immunoblotting. Anc, anchorage; Cyc, cyclin.