FIGURE 3.
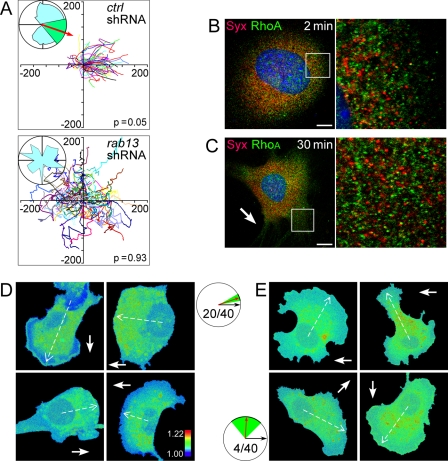
Rab13 was required for directional migration and Syx trafficking. A, ECs in which rab13 had been silenced did not migrate predominantly along the VEGF-A164 0–20 ng/ml gradient (represented by the X+ direction). B and C, rab13 silencing prevented colocalization of Syx and RhoA on endocytic vesicles in VEGF-A164-treated (20 ng/ml) (B) ECs and in ECs subjected to a 0–20 ng/ml VEGF-A164 gradient. (C), Syx and RhoA traffic was normal in ECs transfected by control shRNA (data not shown). D and E, FRET efficiency images of ECs (four cells of 40 in each group) transfected by nontargeting (D) or by rab13-targeted shRNA (E). A solid arrow denotes the direction of the VEGF gradient; a dashed arrow denotes the mean direction of FRET pattern polarization, if such a pattern was manifest. The circular histograms show the average direction (red arrow) and its standard deviation (green sector) for each group, relative to the gradient direction (black arrow). The FRET pattern was polarized in 20 of 40 cells transfected by nontargeting shRNA at a mean direction of 18.4 ± 10.5 degrees, whereas it was polarized only in four of 40 cells transfected by rab13-targeted shRNA at a mean direction of 87 ± 41.8 degrees. Scale bars, 10 μm.