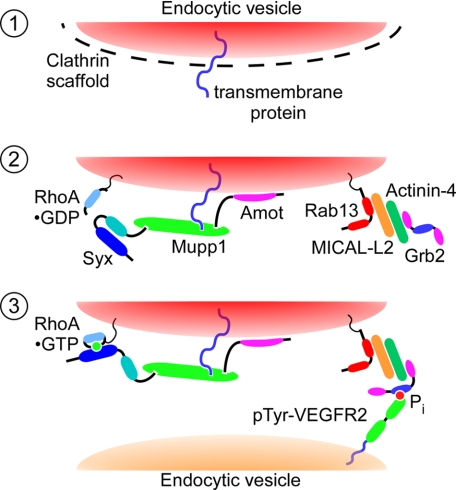
FIGURE 7.
Hypothetical mechanism of Syx and RhoA trafficking from cell junctions to the leading edge. In step 1, VEGF-A binding to VEGFR2 triggers clathrin-dependent endocytosis of junctional transmembrane proteins. Amot targets the Syx-associated complex, containing also Mupp1 and RhoA, to the cytoplasmic leaflet of uncoated endocytic vesicles enclosing the endocytosed junctional transmembrane proteins (step 2). Rab13 associates with and mediates the trafficking of these vesicles. It recruits Grb2 (step 3), which targets the Rab13-associated vesicles to Tyr-phosphorylated VEGFR2. Syx activates RhoA cotrafficking on the same vesicles, at the leading edge of the migrating cell.