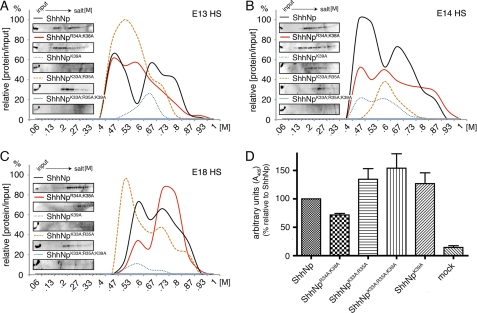
FIGURE 8.
CW residues 33, 35, and 39 selectively interact with HS. A–C, ionic interactions of CW mutant forms ShhNpK33A/R35A/K39A, ShhNpK33A/R35A, and ShhNpK39A with embryonic HS as determined by HS affinity chromatography. Bound proteins were eluted in a 0–1 m NaCl gradient; signal intensity is expressed relative to the signal intensity of the input set to 100%. ShhNpK33A/R35A/K39A did not bind to any HS column, but ShhNpK39A and ShhNpK33A/R35A variably bound to immobilized HS. ShhNpR34A/K38A always bound to all HS preparations. This indicates that residues Lys33, Arg35, and Lys39 contribute to HS binding, Lys39 being the most critical residue. Insets, representative immunoblotted fractions following HS affinity chromatography. D, C3H10T1/2 osteoblast precursor cell differentiation induced by mutant morphogens. C3H10T1/2 cells were stimulated with equivalent amounts of ShhNp, ShhNpR34A/K38A, ShhNpK33A/R35A/K39A, ShhNpK33A/R35A, and ShhNpK39A, and AP activity was quantified. ShhNp AP values were set to 100% in each experiment, and relative values for each mutant form were calculated. The observed increase in biological activity compared with ShhNp was always insignificant (ShhNpK33A/R35A/K39A: 154 ± 25%, p = 0,055, n = 7; ShhNpK33A/R35A: 134 ± 19%, p = 0.0891, n = 7; ShhNpK39A: 127 ± 19%, p = 0.18, n = 7). The observed decrease in ShhNpR34A/K38A biological activity was significant (72 ± 3%, p = 0,0001, n = 7).