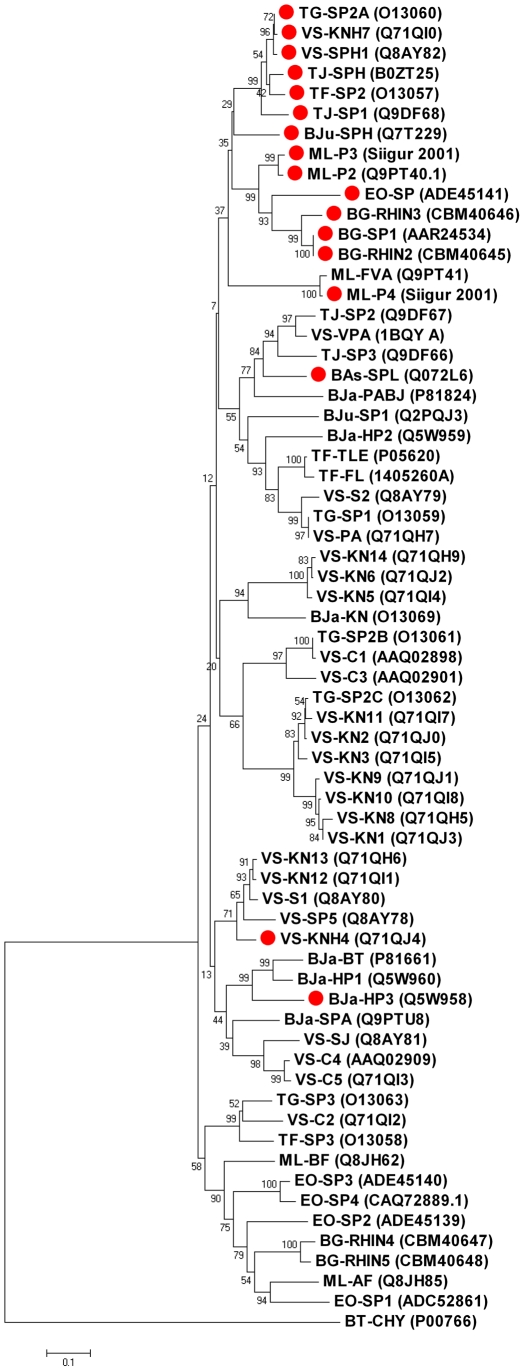
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree showing relationship between serine protease homologues and serine proteases from the same snakes.
65 amino acid sequences from 10 snakes were included together with bovine α-chymotrypsinogen (NCBI accession number: P00766) which was used as an outgroup. The alignment was generated using ClustalW [12] within MEGA 4 [16] using a gap opening penalty of 10 and a gap extension penalty of 0.1 for the initial pairwise alignment, gap opening penalty of 3 and gap extension penalty of 1.8 for the multiple alignment and the Gonnet protein weight matrix. The phylogenetic tree was generated from this within MEGA 4 using the neighbour-joining method and the Jones-Taylor-Thornton substitution model. The bootstrap test was done using 2000 replications. In the diagram sequences are identified using a code which consists of up to 3 characters representing the snake name, (TG: Trimeresurus gramineus; VS: Viridovipera stejnegeri; TJ: Trimeresurus jerdonii; BJu: Bothrops jararacussu ; ML: Macrovipera lebetina; EO: Echis ocellatus; BG: Bitis gabonica; Bja: Bothrops jararaca; TF: Trimeresurus flavoviridis; BAs: Bothrops asper) followed by a dash and then up to 5 characters representing the protein name. Where possible NCBI accession numbers are also included. ML-P3 and ML-P4 sequences were obtained directly from the sequences named VLP3 and VLP4 in [5]. Red circles indicate the sequences with mutations to the catalytic triad.