Table 1.
Rh-catalyzed intramolecular aziridination.
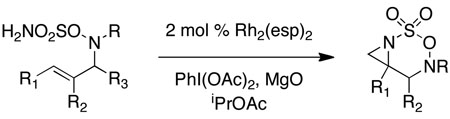 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entrya | substrateb | product | yield | ||
| 1 | 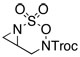 |
64c | |||
| 2 | 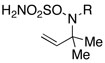 |
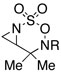 |
R = Troc | 98 | |
| R = Boc | 78 | ||||
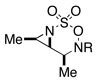
| 3 | 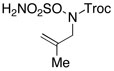 |
 |
94 | ||
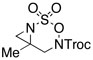
| 4d | 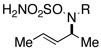 |
 |
R = Troc | 86 | 3:1 dr |
| R = Boc | 82 | 3:1 dr | |||
| R = Mbs | 93 | 13:1 dr | |||
| 5 | 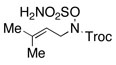 |
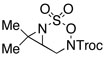 |
82 | ||
| 6 | 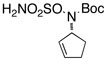 |
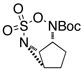 |
65 | ||
| 7 | 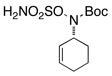 |
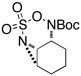 |
51 | ||
Reactions conducted in iPrOAc using 2 mol % Rh2(esp)2, 2.3 equiv of MgO and 1.1 equiv of PhI(OAc)2.
Substrates were prepared using either Mitsunobu or π-allyl Pd chemistry in yields ranging from 60–99%. See supporting information for details.
Isolated yield of this aziridine was reduced due to difficulties associated with its purification. See supporting information for details.
Product diastereomeric ratios determined by 1H NMR integration.
