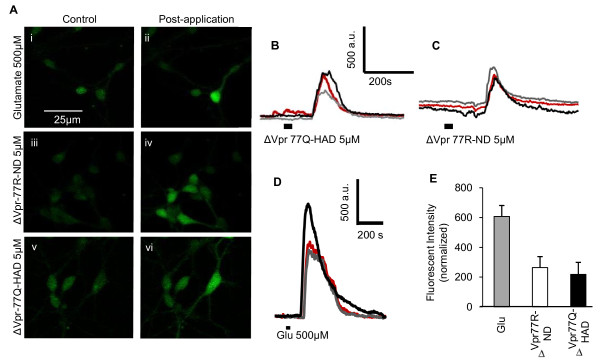
Figure 4.
Vpr peptides (aa 70-96) increase cytosolic Ca2+ fluxes in human neurons. (A) Confocal imaging of Fluo-4-labeled human neurons before and after application of glutamate (i and ii), ΔVpr77R-ND (iii and iv) and ΔVpr77Q-HAD (v and vi) showing an increase in calcium flux for all exposures. (B-D) Representative traces showing time courses of calcium fluxes in human neurons after exposure to glutamate (B), ΔVpr77Q-HAD (C) and ΔVpr77R-ND (D) peptides. The thick black line represents the duration during which glutamate or the peptides were applied. (E) Graphic representation of the relative fluorescent intensity ΔVpr77R-ND and ΔVpr77Q-HAD relative to glutamate response, showing similar levels of fluorescence induction for both peptides (Student t test). Original magnification 200×.