Fig. 2.
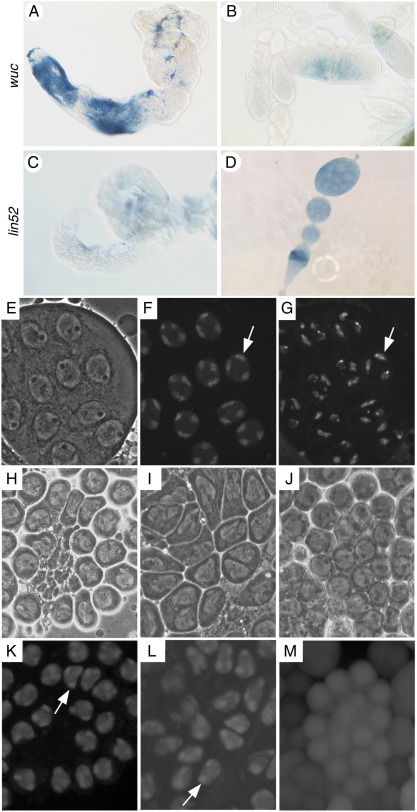
Wuc expression and protein localisation. RNA in situ hybridisation against wuc (A, B) and lin52 (C, D) in testes (A, C) and ovaries (B, D). wuc was detected only in testes; lin52 only in ovaries. Phase contrast (E, H, I, J), eGFP fluorescence (F, K, L, M) and Hoechst 33342 (DNA stain, G) images of wild type (E-G), aly (H, K), achi + vis (I, L) and tomb (J, M) primary spermatocytes expressing eGFP-Wuc. Wuc protein is found predominantly in nuclei, and is concentrated on chromatin in wild type. The three brighter Wuc-eGFP fluorescence domains correspond to the three major chromosome bivalents in each nucleus (arrows, F, G). The three bivalents are more highly labelled than the remainder of the nucleus in most meiotic arrest mutants (arrows K, L). eGFP-Wuc protein does not localise efficiently to the chromatin in tomb mutant spermatocytes, and the label is uniform within the cells (M).