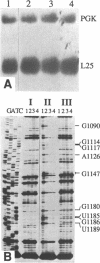
Abstract
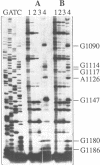
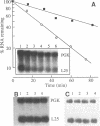
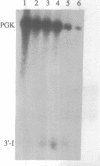
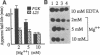
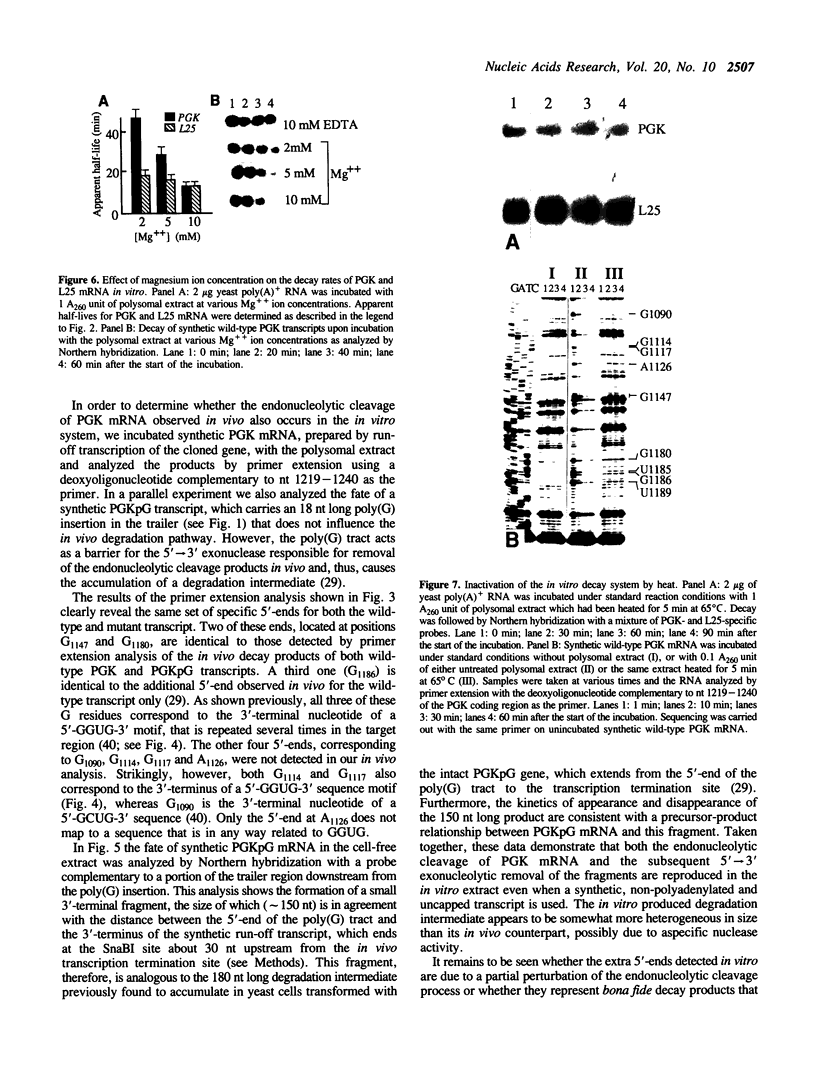
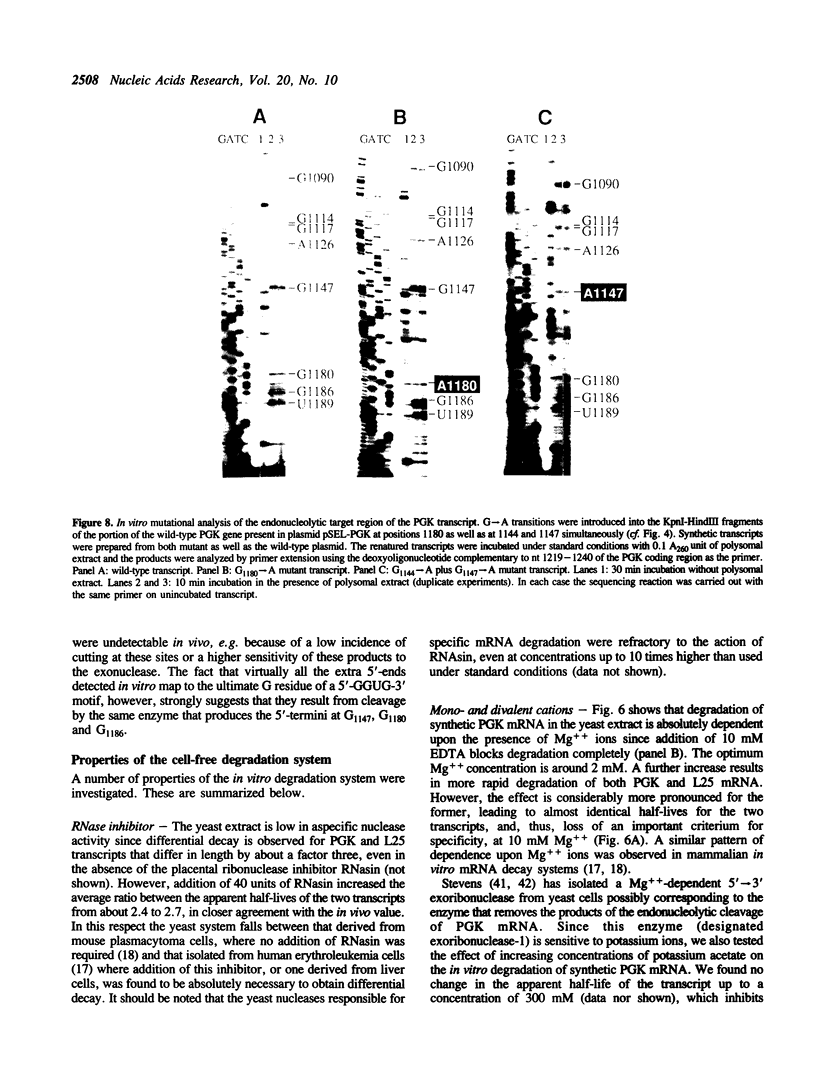
We have isolated a cell-free extract from yeast cells that reproduces the differences observed in vivo in the rate of turnover of individual yeast mRNAs. Detailed analysis of the degradation of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) mRNA in this system demonstrated that both natural and synthetically prepared PGK transcripts are degraded by the same pathway previously established by us in vivo, consisting of endonucleolytic cleavage at a number of 5'-GGUG-3' sequence motifs within a short target region located close to the 3'-end of the coding sequence followed by 5'-3' exonucleolytic removal of the resulting fragments. The extract, therefore, is suitable for studying the mechanistic details of mRNA turnover in yeast. As a first application of this system we have performed a limited mutational analysis of two of the GGUG motifs within the endonucleolytic target region of the PGK transcript. The results show that sequence changes in either motif abolish cleavage at the mutated site only, indicating the involvement of the residues in question in selection of the cleavage positions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwater J. A., Wisdom R., Verma I. M. Regulated mRNA stability. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:519–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay R., Coutts M., Krowczynska A., Brawerman G. Nuclease activity associated with mammalian mRNA in its native state: possible basis for selectivity in mRNA decay. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2060–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Higgins C. F. Mechanisms of mRNA decay in bacteria: a perspective. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. An A + U-rich element RNA-binding factor regulates c-myc mRNA stability in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2460–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Regulation of c-myc mRNA stability in vitro by a labile destabilizer with an essential nucleic acid component. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1996–2006. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. J. Messenger RNA stability in yeast. Yeast. 1989 Jul-Aug;5(4):239–257. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Koeller D. M., Ramin V. C., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA levels requires iron-responsive elements and a rapid turnover determinant in the 3' untranslated region of the mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3693–3699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick D., Parker R., Jacobson A. Identification and comparison of stable and unstable mRNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2269–2284. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Raué H. A., Vreken P., Wilms E., Planta R. J. Mild temperature shock affects transcription of yeast ribosomal protein genes as well as the stability of their mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):7917–7929. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.7917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Hagie F. E., Hayflick J. S., Chen C. Y., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for 3-phosphoglycerate kinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7791–7808. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekema A., Kastelein R. A., Vasser M., de Boer H. A. Codon replacement in the PGK1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: experimental approach to study the role of biased codon usage in gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2914–2924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Hagendoorn M. J., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Structural comparison of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6685–6700. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Pandey N. B. Multiple regulatory steps control histone mRNA concentrations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. B., Marzluff W. F. The stem-loop structure at the 3' end of histone mRNA is necessary and sufficient for regulation of histone mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4557–4559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastori R. L., Moskaitis J. E., Schoenberg D. R. Estrogen-induced ribonuclease activity in Xenopus liver. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10490–10498. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei R., Calame K. Differential stability of c-myc mRNAS in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2860–2868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Brewer G., Groppi V., Ross J. Exonuclease activity that degrades histone mRNA is stable when DNA or protein synthesis is inhibited. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Jun;6(3):227–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Brewer G., Kobs G., Ross J. Substrate specificity of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9382–9388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Ross J. Autogenous regulation of histone mRNA decay by histone proteins in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4345–4356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppel K., Vinci J. M., Baglioni C. The AU-rich sequences in the 3' untranslated region mediate the increased turnover of interferon mRNA induced by glucocorticoids. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):349–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G., Brewer G., Peltz S. W. Properties of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9374–9381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G. H4 histone messenger RNA decay in cell-free extracts initiates at or near the 3' terminus and proceeds 3' to 5'. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):579–593. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgers C. A., Rientjes J. M., van 't Riet J., Raué H. A. rRNA binding domain of yeast ribosomal protein L25. Identification of its borders and a key leucine residue. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90719-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Belasco J. G., Greenberg M. E. Two distinct destabilizing elements in the c-fos message trigger deadenylation as a first step in rapid mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):221–231. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson C. M., Hart P. A., Ross J. Analysis of herpes simplex virus-induced mRNA destabilizing activity using an in vitro mRNA decay system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4459–4465. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Hsu C. L., Isham K. R., Larimer F. W. Fragments of the internal transcribed spacer 1 of pre-rRNA accumulate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacking 5'----3' exoribonuclease 1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):7024–7028. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.7024-7028.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Maupin M. K. A 5'----3' exoribonuclease of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: size and novel substrate specificity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 1;252(2):339–347. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Purification and characterization of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae exoribonuclease which yields 5'-mononucleotides by a 5' leads to 3' mode of hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3080–3085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunitha I., Slobin L. I. An in vitro system derived from Friend erythroleukemia cells to study messenger RNA stability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):560–568. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil E. C. Regulation of ferritin and transferrin receptor mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4771–4774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreken P., van der Veen R., de Regt V. C., de Maat A. L., Planta R. J., Raué H. A. Turnover rate of yeast PGK mRNA can be changed by specific alterations in its trailer structure. Biochimie. 1991 Jun;73(6):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitomer R. S., Montgomery D. L., Nichols D. L., Hall B. D. Transcriptional regulation of the yeast cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3627–3631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel J. J., Bergkamp R. J., Planta R. J., Raué H. A. Effect of deletions in the 5'-noncoding region on the translational efficiency of phosphoglycerate kinase mRNA in yeast. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]