Figure 6.
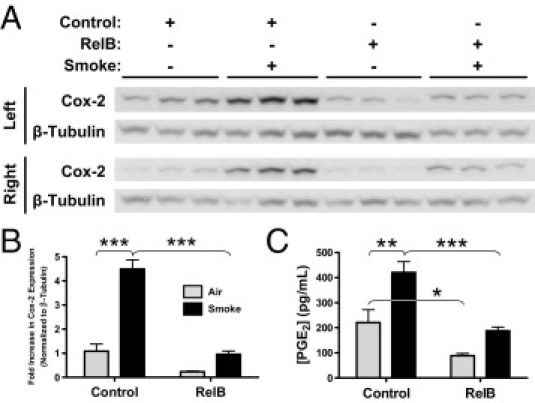
RelB overexpression reduces cigarette smoke–induced Cox-2 expression and PGE2 production. Mice were treated with either the control or RelB virus (two doses of 5 × 108 plaque-forming units per mouse delivered 24 hours apart) and were exposed to either smoke or air (two 1-hour exposures per day for 3 days). A: Cox-2 expression was detected in homogenates of both the left and right lungs using Western blot (n = 3 mice per group). B: Densitometric analysis of both blots confirmed that cigarette smoke significantly increased Cox-2 expression by 4.5-fold and that RelB overexpression before smoke exposure completely dampened this increase (n = 6 per group). C: PGE2 production, detected in the BAL fluids of the same mice, was significantly increased on smoke exposure, but RelB overexpression dampened this increase. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, two-way analysis of variance with a Bonferroni posttest (n = 5 to 6 per group).
