Figure 4. Despite their distinctive molecular surfaces, Patr-AL and HLA-A*0201 bind peptides in similar conformation.
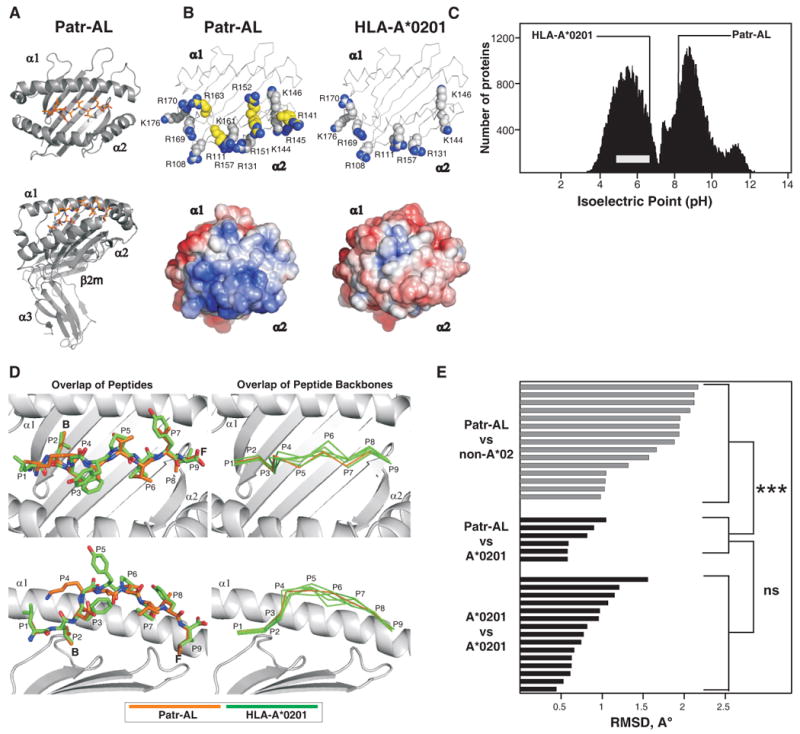
(A) Ribbon diagrams of the crystallographic structure of the complex of peptide ALDKATVLL (colored red) bound to Patr-AL. The upper diagram is a top view showing the peptide bound by the α1and α2 domains. The lower diagram is a side view showing all four extracellular Patr-AL domains.(B) Compares the distribution of electropositive residues on the top face of Patr-AL (PDB ID pending) and HLA-A*0201(PDB ID 1HHK). The upper diagrams show the position of positively-charged residues; those unique to Patr-AL colored yellow. In the lower diagrams, Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatic potentials of Patr-AL and HLA-A*0201 are projected onto solvent-exposed surfaces and colored from red (-5.0) to blue (+5.0). (C) Compares the isoelectric point of Patr-AL to those of other cellular proteins. The bimodal black-shaded distribution represents all cellular proteins (88), the grey bar shows the range of isoelectric point for MHC class I other than Patr-AL. The isoelectric points of Patr-AL and HLA-A*02 are indicated by the lines. (D) Visual comparison of the conformation of peptide bound by Patr-AL and HLA-A*020. The left panels show least-squares superimposition of Patr-AL and HLA-A*0201 peptide-binding domains, which results in close alignment of peptide Cα backbones and similar side chain orientations. The positions of peptide residues and pockets B and F are indicated. The right panels show alignment of the Patr-AL bound peptide backbone with its counterparts in six structures of different peptides bound to HLA-A*0201 (PDB IDs 1HHK, 1QEW, 1B0G, 1HHI, 1HHG, 1HHJ). (E) Quantitative comparison of the conformation of peptide bound to Patr-AL and HLA class I. RMSDs of the Cα backbone for Patr-AL bound peptides fall within the range observed for HLA-A*0201 peptides, and are significantly lower than for peptides bound to non-A*02 HLA class I. structures. The details of the allotypes and peptides compared are in supplementary Fig. S5.
