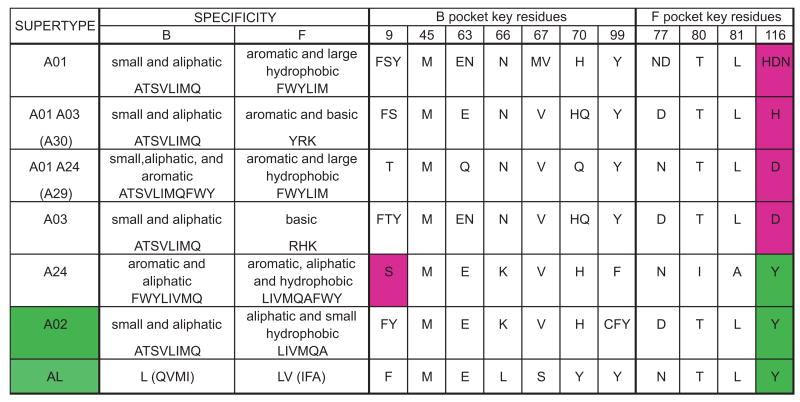
Figure 6. The A02 supertype can be simply described by the residues at positions 9 and 116 of the peptide binding domain.
Shown are the supertypes defined by Sidney et al (68), the characteristics of the residues accommodated by the B and F pockets and the amino acids found at the key residues of these pockets for all allotypes. All allotypes assigned to a supertype were aligned and the amino acids present at the key residue positions were determined; they are shown using the single letter code. Only A02 and A24 can accommodate aliphatic residues in the F pocket, a feature correlating with the presence of tyrosine at position 116 of the peptide-binding domain (highlighted green in the figure). They differ in the residues that can be accommodated in the B pocket, with A24 able to accommodate aromatic residues, a distinction that correlates with the presence of serine at position 9 of the peptide-binding domain (highlighted purple).